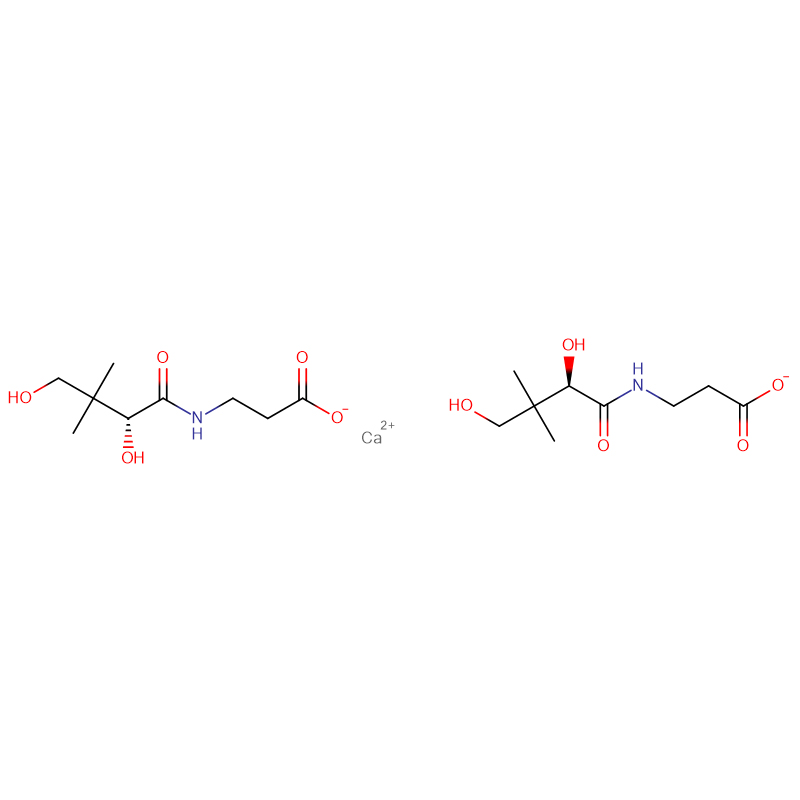
Vitamin B5 (Calcium Pantothenate) Cas: 137-08-6
| Catalog Number | XD91865 |
| Product Name | Vitamin B5 (Calcium Pantothenate) |
| CAS | 137-08-6 |
| Molecular Formula | C9H17NO5.1/2Ca |
| Molecular Weight | 476.53 |
| Storage Details | 2-8°C |
| Harmonized Tariff Code | 29362400 |
Product Specification
| Appearance | White powder |
| Assay | 99% min |
| Melting point | 190 °C |
| alpha | 26.5 º (c=5, in water) |
| refractive index | 27 ° (C=5, H2O) |
| Fp | 145 °C |
| solubility | H2O: 50 mg/mL at 25 °C, clear, nearly colorless |
| PH | 6.8-7.2 (25℃, 50mg/mL in H2O) |
| optical activity | [α]20/D +27±2°, c = 5% in H2O |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water. |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Stability | Stable, but may be moisture or air sensitive. Incompatible with strong acids, strong bases. |
It can be applied to biochemical studies; as the nutrient composition of tissue culture medium. It is clinically used for the treatment of vitamin B deficiency, peripheral neuritis and postoperative colic.
2. It can be used as food fortifier, also used as infant food with the usage amount of 15~28 mg/kg; it is 2~4mg/kg in the drink.
3. This product is a vitamin drugs, being an integral part of coenzyme A. In the mixture of calcium pantothenate, only the right-hand body has vitamin activity, participating into the in vivo metabolism of protein, fat and carbohydrate. It can be used for the treatment of vitamin B deficiency and peripheral neuritis, and postoperative colic. Its combined treatment with vitamin C can be used for the treatment of disseminated lupus erythematosus. The lack of calcium pantothenate in human body has the following symptoms: (1) growth arrest, weight loss and sudden death. (2) Skin and hair disorders. (3) Neurological disorders. (4) Digestive disorders, liver dysfunction. (5) Affect the antibody formation. (6) Kidney dysfunction. Every day the body demands 5 mg of calcium pantothenate (calculated based on pantothenic acid). Calcium pantothenate, as a nutritional supplement, can be used for the food processing. In addition to special nutritional food, the usage amount should be below 1% (calculated on calcium) (Japan). Upon the strengthening of the milk powder, the usage amount should be 10 mg/100g. Addition of 0.02% into the Shochu and whiskey can further enhance the flavor. Addition of 0.02% into the honey can prevent the winter crystallization. It can be used for buffering the bitterness of caffeine and saccharin.
4. It can be used as feed additives, food additives, being in line with Pharmacopoeia USP28/BP2003
5. It can be used as nutritional supplements, being able to enhance the flavor of shochu whiskey to prevent the crystallization of honey in winter.
6. It is the precursor product for the biosynthesis of coenzyme A. Because of the easy-deliquescence of pantothenic acid and other unstable properties, it is used of calcium salt as the substitute.
(+)-Pantothenic acid calcium salt is a member of the B complex vitamins; essential vitamin for the biosynthesis of coenzyme A in mammalian cells. Occurs ubiquitously in all animal and plant tissue. The richest common source is liver, but jelly of the queen bee contains 6 times as much as liver. Rice bran and molasses are other good sources.
Calcium pantothenate is used as an emollient and to enrich creams and lotions in hair care preparations. This is the calcium salt of pantothenic acid found in liver, rice, bran, and molasses. It is also found in large amounts in royal jelly.
Calcium Pantothenate is a nutrient and dietary supplement which is the calcium chloride double salt of . It is a white powder of bitter taste and has a solubility of 1 g in 3 ml of water. It is used in special dietary foods.
The only therapeutic indication for pantothenic acid is intreatment of a known or suspected deficiency of this vitamin.Because of the ubiquitous nature of pantothenic acid, deficiencystates of this vitamin are only seen experimentally byuse of synthetic diets devoid of the vitamin, by use of thevitamin antagonist, ω-methylpantothenic, or both. In a 1991review, Tahiliani and Beinlich described that the mostcommon symptoms associated with pantothenic acid deficiencywere headache, fatigue, and a sensation of weakness.Sleep disturbances and gastrointestinal disturbances, amongothers, were also noted. The most likely setting for pantothenicacid deficiency is in the setting of alcoholism wherea multiple vitamin deficiency exists confounding the exactrole of the pantothenic acid deficiency as compared to theother vitamins. Because a deficiency of a single B vitamin israre, pantothenic acid is commonly formulated in multivitaminor B-complex preparations.