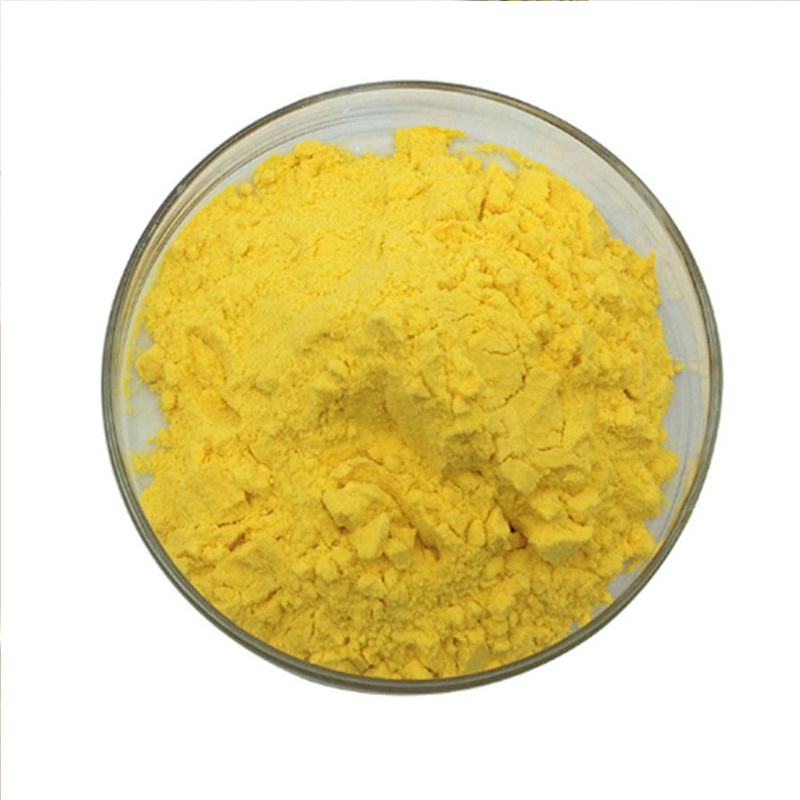
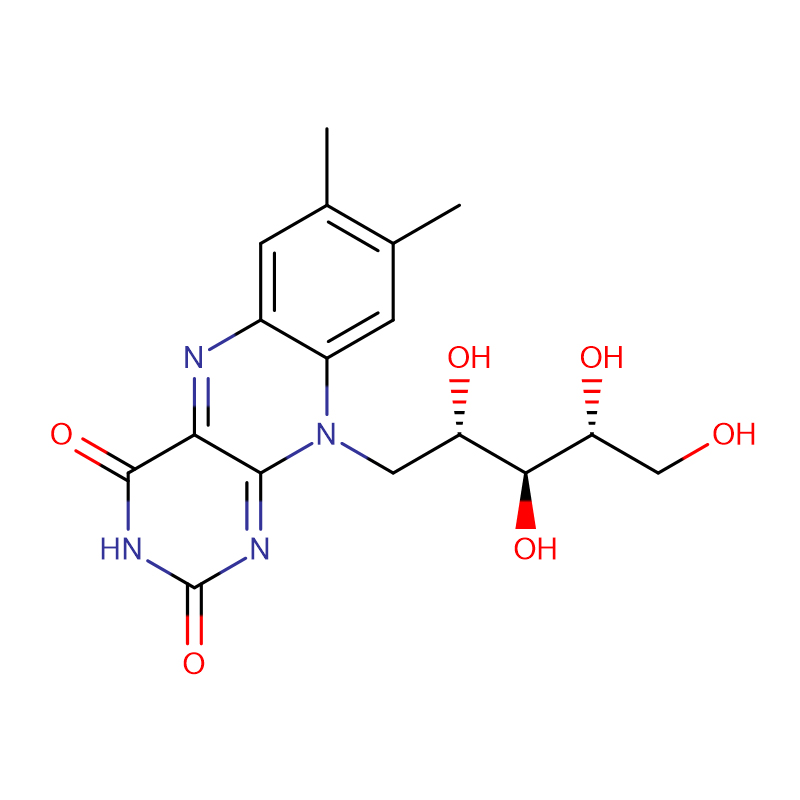
Vitamin B2 Riboflavin Cas: 83-88-5
| Catalog Number | XD91863 |
| Product Name | Vitamin B2 Riboflavin |
| CAS | 83-88-5 |
| Molecular Formula | C17H20N4O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 376.36 |
| Storage Details | 2-8°C |
| Harmonized Tariff Code | 29362300 |
Product Specification
| Appearance | Yellow crystal powder |
| Assay | 99% min |
| Melting point | 290 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| alpha | -135 º (c=5, 0.05 M NaOH) |
| Boiling point | 504.93°C (rough estimate) |
| density | 1.2112 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | -135 ° (C=0.5, JP Method) |
| Fp | 9℃ |
| solubility | Very slightly soluble in water, practically insoluble in ethanol (96 per cent). Solutions deteriorate on exposure to light, especially in the presence of alkali. It shows polymorphism (5.9). |
| pka | 1.7(at 25℃) |
| Odor | Slight odour |
| PH | 5.5-7.2 (0.07g/l, H2O, 20°C) |
| PH Range | 6 |
| Water Solubility | 0.07 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
| Stability | Stable, but light-sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, reducing agents, bases, calcium, metallic salts. May be moisture sensitive. |
Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) is produced by yeast from glucose, urea, and mineral salts in an aerobic fermentation.
Nutritional factor found in milk, eggs, malted barley, liver, kidney, heart, leafy vegetables. Richest natural source is yeast. Minute amounts present in all plant and animal cells. Vitamin (enzyme cofactor).
Vitamin B2; Vitamin cofactor; LD50(rat) 560 mg/kg ip.
riboflavin (Vitamin B2) is used in skin care preparations as an emollient. It can be found in sun care products as a suntan enhancer. Medicinally, it is used for the treatment of skin lesions.
Riboflavin is the water-soluble vitamin b2 required for healthy skin and the building and maintaining of body tissues. it is a yellow to orange-yellow crystalline powder. it acts as a coenzyme and carrier of hydrogen. it is stable to heat but may dissolve and be lost in cooking water. it is relatively stable to storage. sources include leafy vegetables, cheese, eggs, and milk.
Severe riboflavin deficiency is known as ariboflavinosis, andtreatment or prevention of this condition is the only provenuse of riboflavin. Ariboflavinosis is most commonly associatedwith multiple vitamin deficiency as a result of alcoholismin developed countries. Because of the large numberof enzymes requiring riboflavin as a coenzyme, deficienciescan lead to a wide range of abnormalities. In adults seborrheicdermatitis, photophobia, peripheral neuropathy, anemia, andoropharyngeal changes including angular stomatitis, glossitis,and cheilosis, are often the first signs of riboflavin deficiency.In children, cessation of growth can also occur. As the deficiencyprogresses, more severe pathologies develop untildeath ensues. Riboflavin deficiency may also produce teratogeniceffects and alter iron handling leading to anemia.