Tricine, is a zwitterionic buffer reagent whose name is derived from Tris and glycine. Its structure is similar to Tris, but its high concentration has weaker inhibitory activity than Tris. One of Good's buffer reagents, originally developed to provide a buffer system for chloroplast reactions. The effective pH buffer range of Tricine is 7.4-8.8, pKa=8.1 (25 °C), and it is commonly used as a running buffer and for resuspending cell pellets. Tricine has the characteristics of low negative charge and high ionic strength, which is very suitable for electrophoretic separation of low molecular weight proteins of 1~100 kDa. In the firefly luciferase-based ATP assay, comparing 10 common buffers, Tricine (25 mM) showed the best detection effect. In addition, Tricine is also an effective hydroxyl radical scavenger in free radical-induced membrane damage experiments.


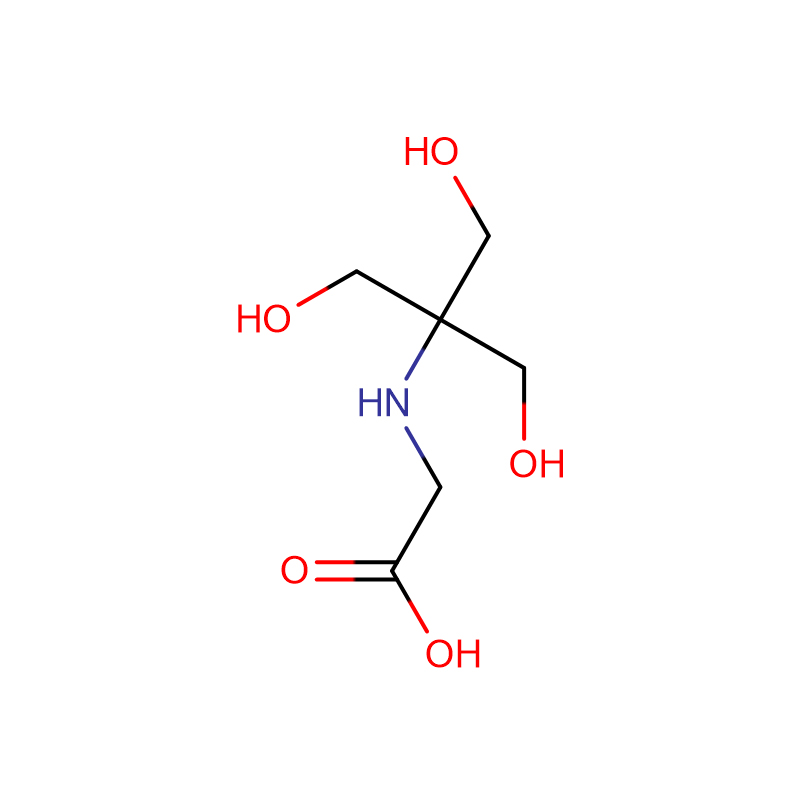
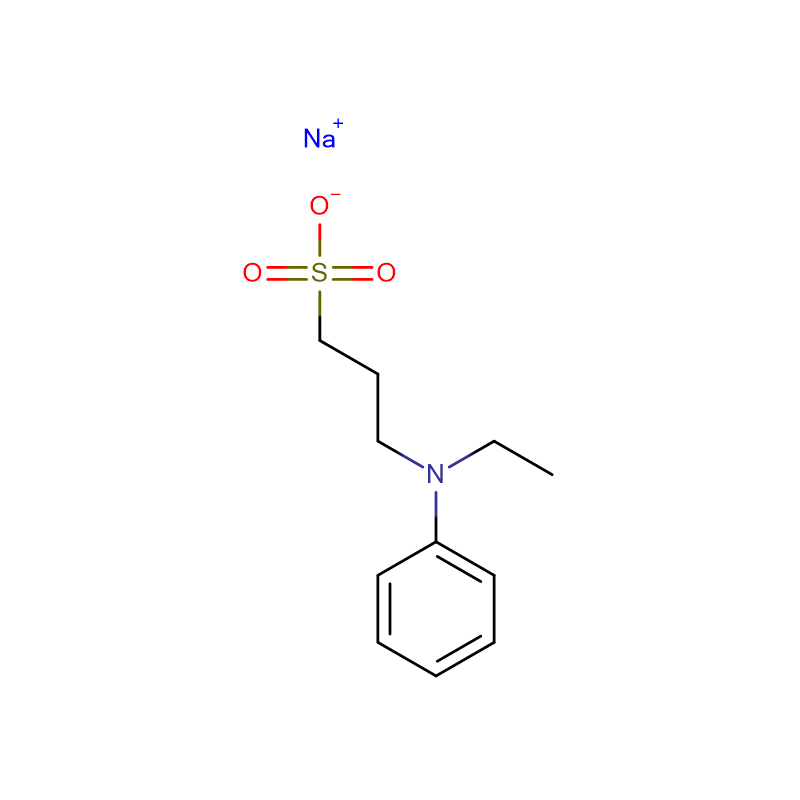
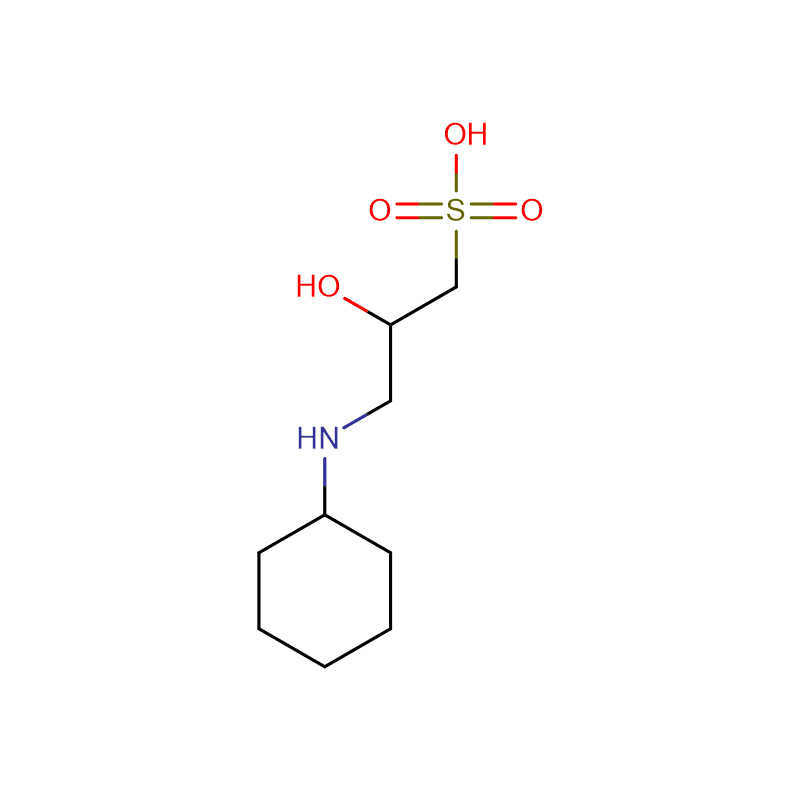
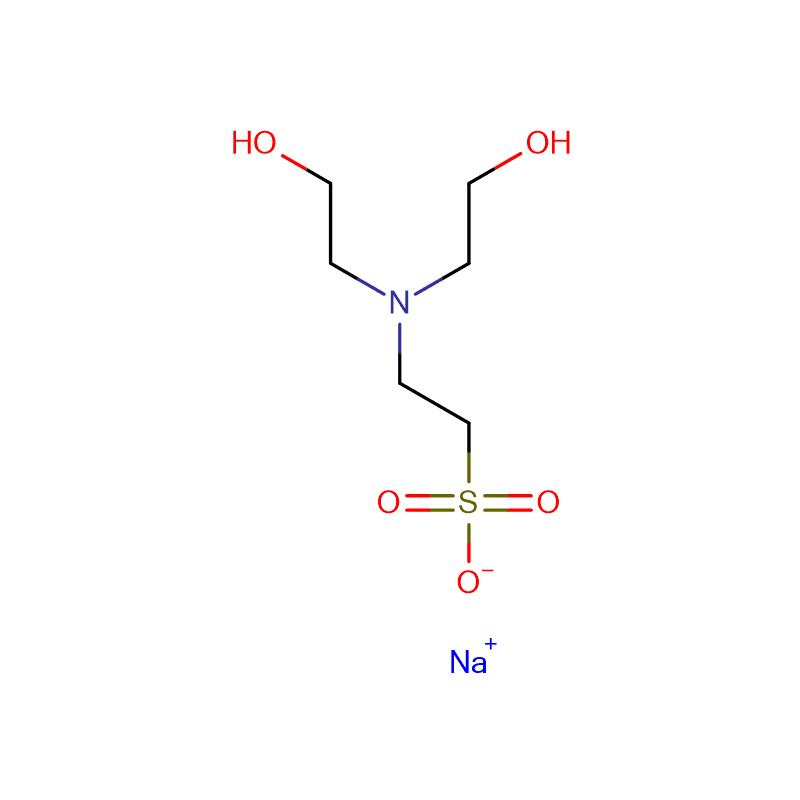
![Bis[2-Hydroxyethyl] imino Tris-(Hydroxymethyl)-methane Cas: 6976-37-0 99%](https://cdn.globalso.com/xdbiochems/6976-37-0.jpg)