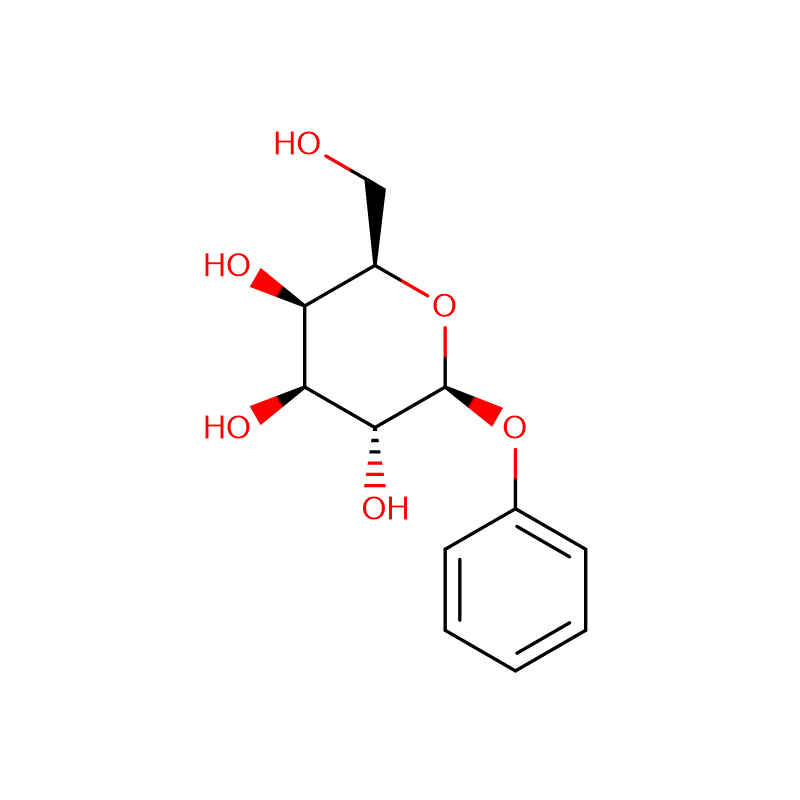
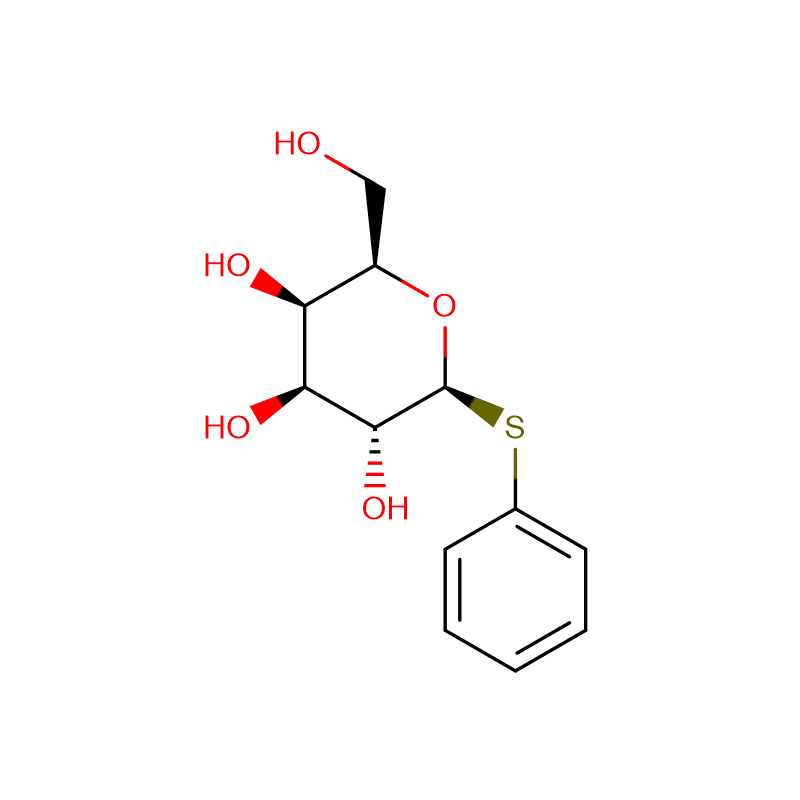
Phenylgalactoside Cas:2818-58-8 99% White to off-white crystalline powder
| Catalog Number | XD90041 |
| Product Name | Phenylgalactoside |
| CAS | 2818-58-8 |
| Molecular Formula | C12H16O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 256.25 |
| Storage Details | Ambient |
Product Specification
| Apperance | White to off-white crystalline powder |
| Storage Temp | - 10 °C |
| Density | 1.2993 (rough estimate) |
| Melting Point | 146.0 to 149.0 deg-C |
| Boiling Point | 359.49°C (rough estimate) |
| Refractive Index | -42 ° (C=2.3, H2O) |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents |
| Assay | 99% |
Galactosidase refers to a class of enzymes that hydrolyze substances containing galactosidic bonds, such as lactose (lactose is a disaccharide formed by the dehydration condensation of one molecule of glucose and one molecule of galactose). Mainly divided into α-galactosidase and β-galactosidase. α-Galactosidase catalyzes the hydrolysis of α-galactosidase bonds, which can convert and decompose the anti-nutritional factors α-galactosides in feed and soy food, and improve their nutritional content. In addition, the enzyme also has certain applications in the pharmaceutical, thickener processing and paper industries. β-Galactosidase is not only used more and more widely in the food industry, but also plays an important role in the fields of biotechnology such as genetic engineering, enzyme engineering, protein engineering, etc., and has begun to be widely used in medicine and other fields.
α-galactosidase (α-galactosidase, α-gal, EC 3.2.1.22) is an exoglycosidase that catalyzes the hydrolysis of α-galactosidic bonds, and is also known as melibiase because it can decompose melibiose , which catalyzes the hydrolysis of α-galactosidic bonds. This feature makes it useful for improving and eliminating anti-nutrients in feed and soy foods. In addition, it can realize B→O blood group conversion in the medical field, prepare universal blood type, and also play an important role in the enzyme replacement therapy of Fabry disease. Alpha-galactosidase can also act on complex polysaccharides, glycoproteins and sphingolipids containing alpha-galactosidic bonds. Some α-galactosidase enzymes also have the effect of transgalactosylation when the substrate concentration is highly enriched, which can be used for the synthesis of oligosaccharides and the preparation of cyclodextrin derivatives. The development of neutrophilic or pH-stable α-galactosidase and the search for microorganisms or plants with high enzyme production have become a research hotspot in recent years. Many thermostable α-galactosidases have also gradually attracted wide interest of scientists due to their special properties, expecting to use their thermostability to play a greater role in industrial applications, as well as to show broader application in the fields of science and technology and medicine. application prospects.