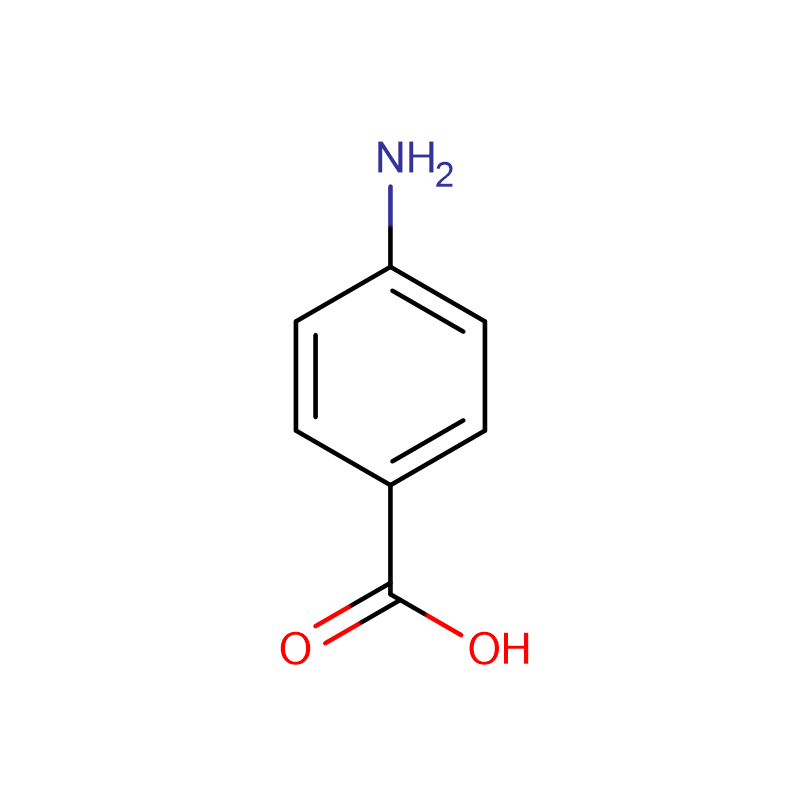
PABA Cas:150-13-0
| Catalog Number | XD91210 |
| Product Name | PABA |
| CAS | 150-13-0 |
| Molecular Formula | C7H7NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 137.14 |
| Storage Details | Ambient |
| Harmonized Tariff Code | 29224985 |
Product Specification
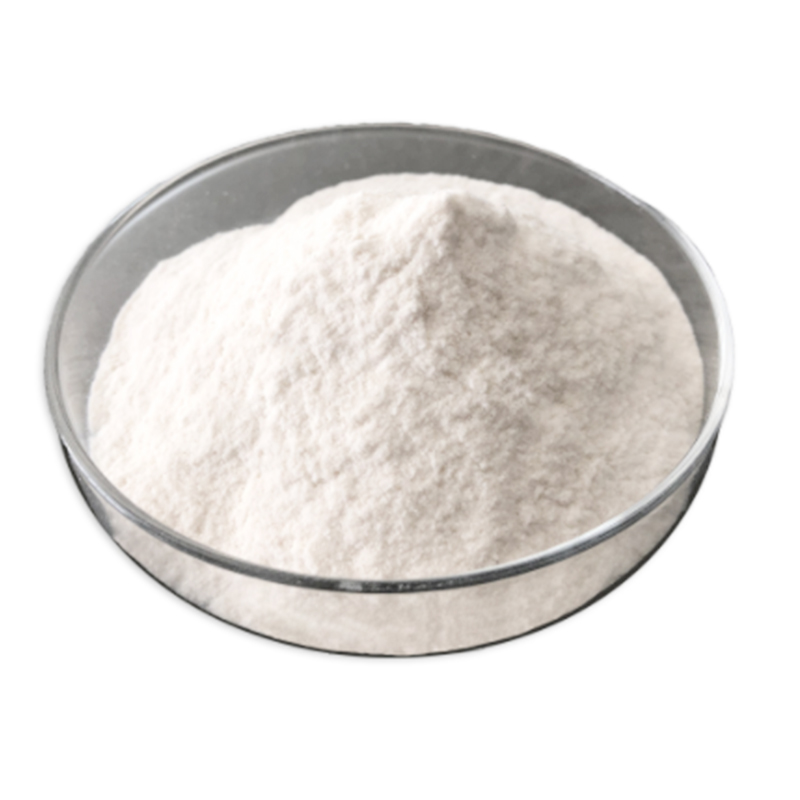
| Appearance | White or off-white crystalline powder |
| Assay | 99% min |
| Loss on Drying | <0.2% |
| Residue on Ignition | <0.1% |
| Melting Range | 186 -189°C |
| Ordinary Impurities | <1% |
| Heavy Metal | <0.002% |
| Volatile diazoizable substances | <0.002% |
4-Aminobenzoic acid (also known as para-aminobenzoic acid or PABA because the two functional groups are attached to the benzene ring across from one another in the para position) is an organic compound with the formula H2NC6H4CO2H. PABA is a white solid, although commercial samples can appear gray. It is slightly soluble in water. It consists of a benzene ring substituted with amino and carboxyl groups. The compound occurs extensively in the natural world.
4-Aminobenzoic acid is an intermediate in the synthesis of folate by bacteria, plants, and fungi.
PABA finds use mainly in the biomedical sector. Other uses include its conversion to specialty azo dyes and crosslinking agents. PABA is also used as a biodegradable pesticide, though its use is now limited due to evolution of new variants of bio-pesticides.