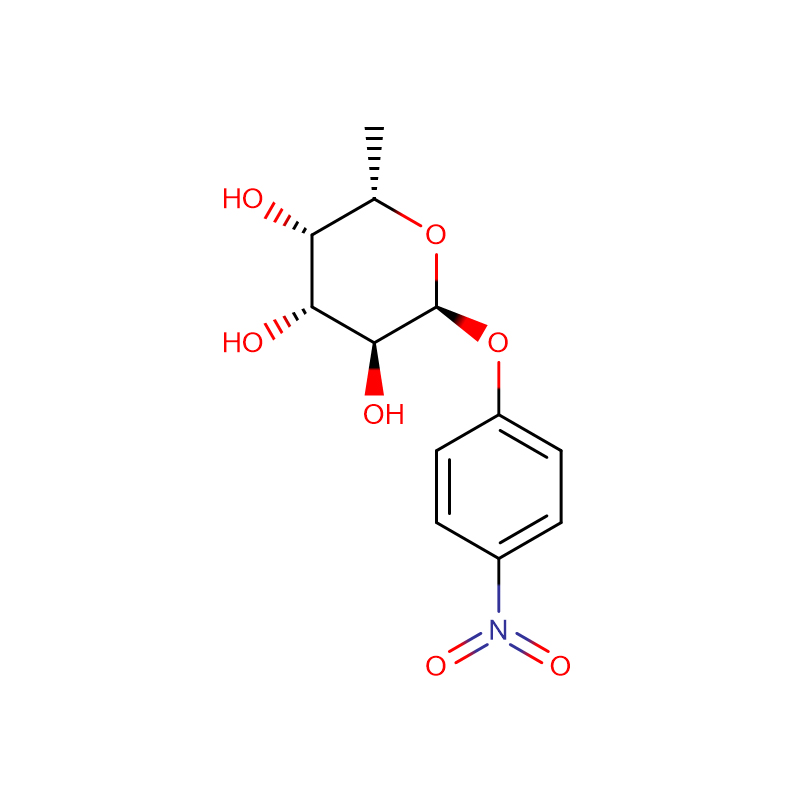
p-Nitrophenyl -a-L-Fucopyranoside Cas:10231-84-2 White to pale yellow crystalline powder
| Catalog Number | XD90142 |
| Product Name | p-Nitrophenyl -a-L-Fucopyranoside |
| CAS | 10231-84-2 |
| Molecular Formula | C12H15NO7 |
| Molecular Weight | 285.25 |
| Storage Details | 2 to 8 °C |
| Harmonized Tariff Code | 29400000 |
Product Specification
| Appearance | White to pale yellow crystalline powder |
| Assay | 99% |
| TLC | Single spot |
| Purity HPLC | Min 98% |
| Solubility (1 % in water) | Clear colourless solution |
| Density | 1.503±0.06 g/cm3 (20 ºC 760 Torr), |
| Melting point | 196-197 ºC |
| Boiling point | 515.4°Cat760mmHg |
| Flash point | 265.5°C |
| Refractive index | 1.623 |
LecA (PA-IL) is a cytotoxic lectin and adhesin produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa which binds hydrophobic galactosides with high specificity and affinity. By using a lecA-egfp translation fusion and immunoblot analysis of the biofilm extracellular matrix, we show that lecA is expressed in biofilm-grown cells. In static biofilm assays on both polystyrene and stainless steel, biofilm depth and surface coverage was reduced by mutation of lecA and enhanced in the LecA-overproducing strain PAO-P47. Biofilm surface coverage by the parent strain, PAO-P47 but not the lecA mutant on steel coupons was also inhibited by growth in the presence of either isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside (IPTG) or p-nitrophenyl-alpha-D-galactoside (NPG). Furthermore, mature wild-type biofilms formed in the absence of these hydrophobic galactosides could be dispersed by the addition of IPTG. In contrast, addition of p-nitrophenyl-alpha-L-fucose (NPF) which has a high affinity for the P. aeruginosa LecB (PA-IIL) lecti n had no effect on biofilm formation or dispersal. Planktonic growth of P. aeruginosa PAO1 was unaffected by the presence of IPTG, NPG or NPF, nor was the strain able to utilize these sugars as carbon sources, suggesting that the observed effects on biofilm formation were due to the competitive inhibition of LecA-ligand binding. Similar results were also obtained for biofilms grown under dynamic flow conditions on steel coupons, suggesting that LecA contributes to P. aeruginosa biofilm architecture under different environmental conditions.
An alpha-L-fucosidase (EC 3.2.1.51) able to release the t-fucosyl residue from the side chain of xyloglucan oligosaccharides has been detected in the leaves of Arabidopsis plants. Moreover, an alpha-L-fucosidase with similar substrate specificity was purified from cabbage (Brassica oleracea) leaves to render a single band on SDS-PAGE. Two peptide sequences were obtained from this protein band, and they were used to identify an Arabidopsis gene coding for an alpha-fucosidase that we propose to call AtFXG1. In addition, an Arabidopsis gene with homology with known alpha-L-fucosidases has been also found, and we proposed to name it as AtFUC1. Both AtFXG1 and ATFUC1 were heterologously expressed in Pichia pastoris cells and the alpha-L-fucosidase activities secreted to the culture medium. The alpha-L-fucosidase encoded by AtFXG1 was active against the oligosaccharides from xyloglucan XXFG as well as against 2'-fucosyl-lactitol but not against p-nitrophenyl-alpha-L-fucopyranoside. However, the AtFUC1 heterologously expressed was active only against 2'-fucosyl-lactitol. Thus, the former must be related to xyloglucan metabolism.