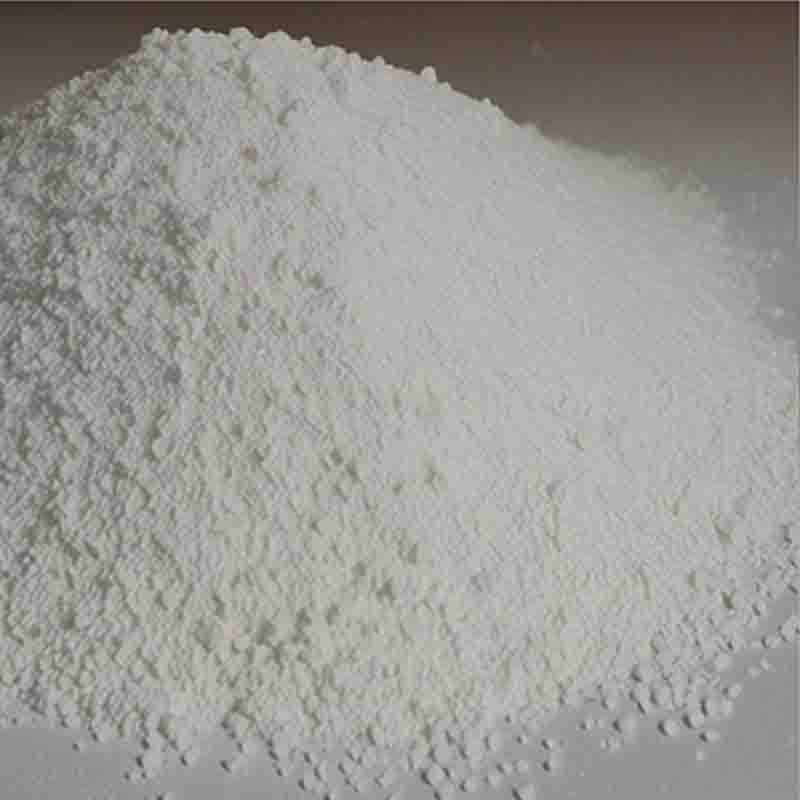
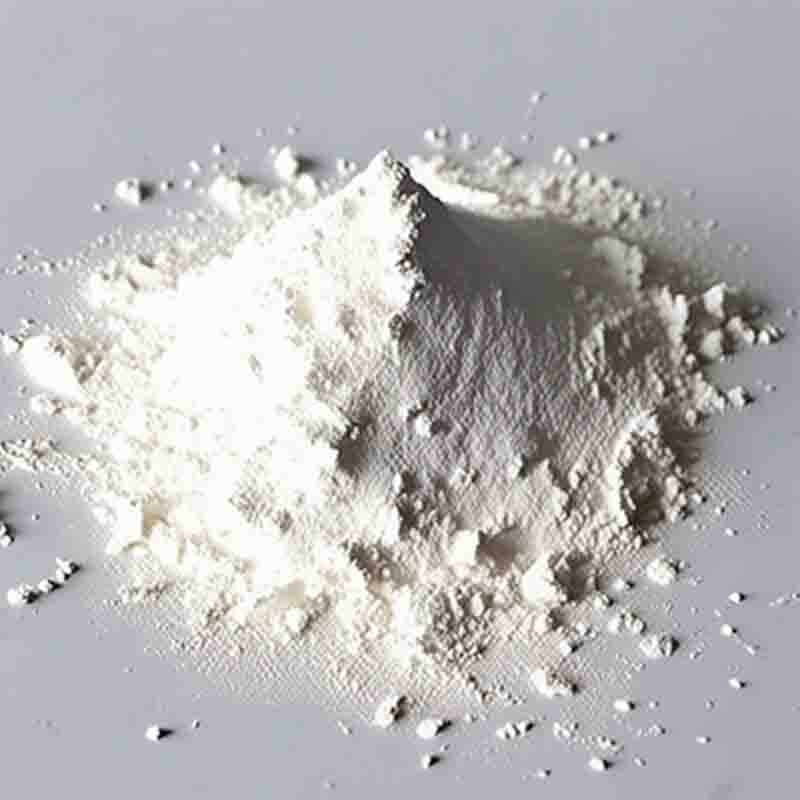
N,N’-Di(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazine CAS: 122-96-3
| Catalog Number | XD94068 |
| Product Name | N,N'-Di(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazine |
| CAS | 122-96-3 |
| Molecular Formula | C8H18N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 174.24 |
| Storage Details | Ambient |
Product Specification
| Appearance | White powder |
| Assay | 99% min |
N,N'-Di(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazine (HEP) is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C10H24N2O2. It is a clear, colorless liquid that possesses two hydroxyethyl groups attached to a piperazine ring structure. HEP finds widespread use in various industries due to its unique properties and functional groups.In the pharmaceutical industry, N,N'-di(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazine is commonly employed as a building block or intermediate in the synthesis of various drugs. It serves as a precursor for the preparation of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) that exhibit diverse physiological effects. The presence of hydroxyethyl groups in HEP allows for further functionalization to modify the properties and bioactivity of the resulting compounds. HEP is particularly utilized in the production of antihistamines, antihypertensive agents, and anticancer drugs.Additionally, HEP is an essential component in the production of a class of chemicals called quaternary ammonium compounds (QUATs). QUATs have significant applications as surfactants, disinfectants, and fabric softeners. HEP functions as a key ingredient in the synthesis of QUATs due to its ability to form positively charged ions when reacted with alkyl halides or fatty acids. These positively charged ions provide excellent detergent properties and antimicrobial activity, making HEP-derived QUATs widely used in household cleaning products, fabric conditioners, and water treatment solutions.HEP is also utilized in the production of polyurethane-based foams and coatings. Its unique structure and functional groups enable it to act as a chain extender or crosslinking agent in the polymerization process. By incorporating HEP into the polyurethane synthesis, the resulting polymers exhibit improved flexibility, durability, and thermal stability. These properties make HEP an essential ingredient in the manufacturing of foams used in insulation, cushioning, and packaging, as well as coatings employed in adhesives, sealants, and paints.Furthermore, HEP finds applications in the field of corrosion inhibition. Its capability to form complexes with metal ions allows it to create a protective layer over metal surfaces, preventing corrosion. HEP-based corrosion inhibitors are utilized in various industries, including oil and gas, water treatment, and automotive, to protect metal equipment and structures from degradation caused by exposure to corrosive environments.In conclusion, N,N'-di(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazine (HEP) is a versatile compound with wide-ranging applications in the pharmaceutical, surfactant, polymer, and corrosion inhibition industries. Its hydroxyethyl groups enable it to serve as a crucial building block for drug synthesis, a key component in the production of QUATs, a crosslinking agent in polymer chemistry, and a corrosion inhibitor. HEP's diverse functionalities make it a valuable compound in these industries, contributing to the development of innovative products and solutions.






![D-erythro-Hexonic acid, 2,4,6-trideoxy-3,5-O-(1-methylethylidene)-6-[(5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)sulfonyl]-, 1,1-dimethylethyl ester CAS: 1326302-97-9](https://cdn.globalso.com/xdbiochems/白色粉末2134.jpg)

