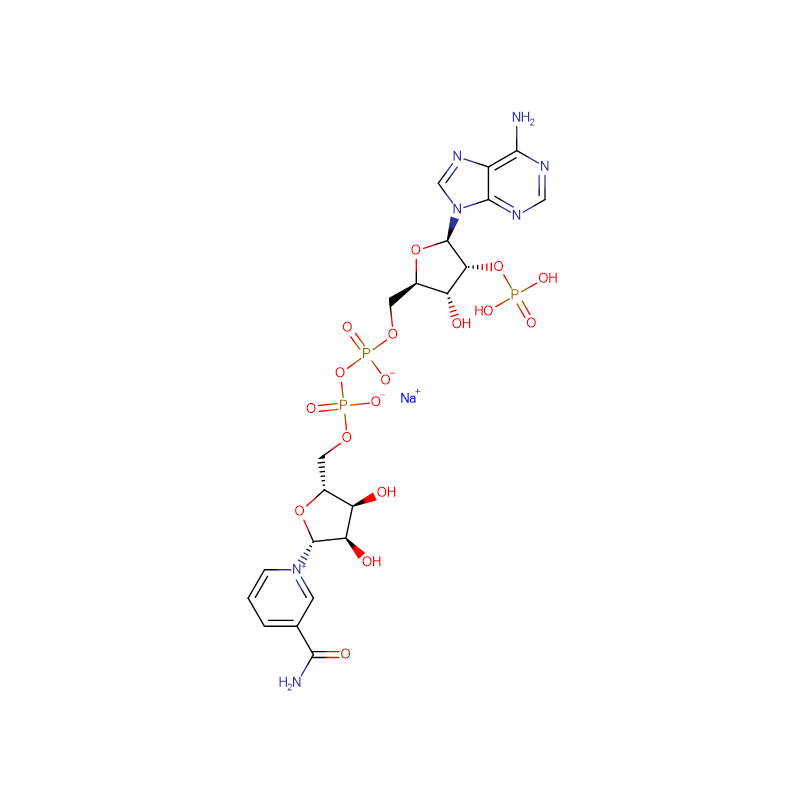
Nicotinamide Riboside Cas: 1341-23-7
| Catalog Number | XD91951 |
| Product Name | Nicotinamide Riboside |
| CAS | 1341-23-7 |
| Molecular Formula | C11H15N2O5+ |
| Molecular Weight | 255.25 |
| Storage Details | Ambient |
| Harmonized Tariff Code | 2933199090 |
Product Specification
| Appearance | White powder |
| Assay | 99% min |
Nicotinamide Riboside can be used in biological study of gene circadian reprogramming transcriptome in liver identified metabolic pathways of aging in mouse. It also increases NAD+ in the cerebral cortex and reduces cognitive deterioration in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is a critical coenzyme that, when reduced to NADH, serves as a reducing agent to donate electrons for oxidative phosphorylation and ATP synthesis in mitochondria. NAD+ is a critical cofactor for enzymes such as sirtuins, ADP-ribosyltransferases (ARTs), and Poly [ADP- ribose] polymerases (PARPs) and is continuously consumed by these enzymes. The NAD+/NADH ratio is a critical component of the redox state of the cell. (Verdin 2015). By some counts, NAD or the related NADP participates in a quarter of all cellular reactions (Opitz Heiland 2015). There are separate compartments of NAD+ in the nucleus, mitochondria, and cytoplasm (Verdin 2015).
Nicotinamide riboside (NR) can be converted into NAD+ through an intermediate step in which it is converted into nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) by NR kinase (Nrk) and then to NAD+ by NMNATs. NR is naturally found in some foods but at very low quantities (e.g. low micromolar range). Historically, NR was difficult to obtain in large purified amounts, but thanks to advances in synthesis methods (Yang 2007), as of June 2013, it is sold as a dietary supplement.