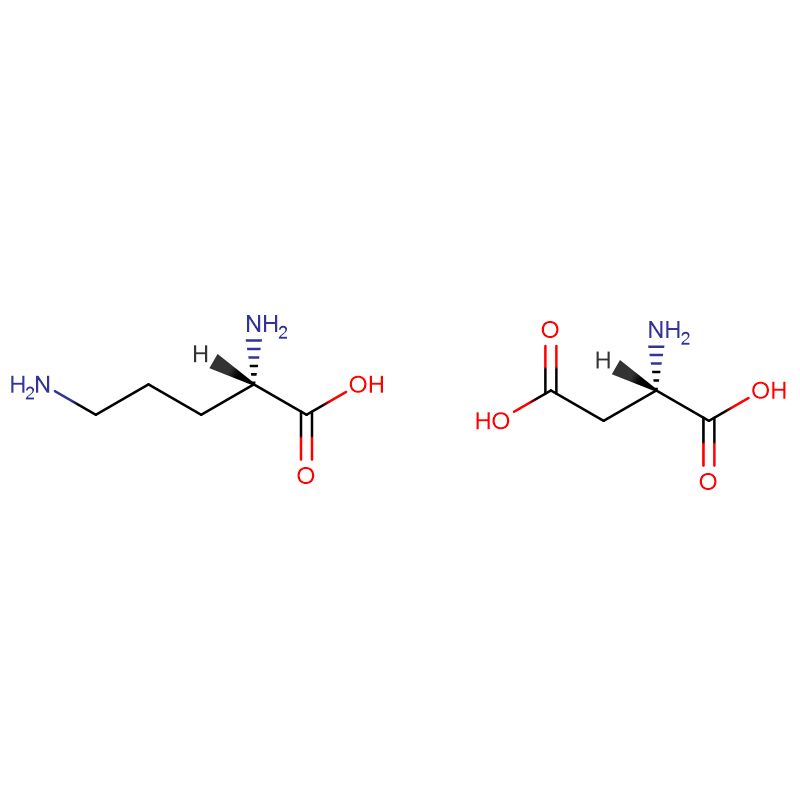
L-Ornithine L-Aspartate Cas:3230-94-2
|
Catalog Number |
XD91158 |
|
Product Name |
L-Ornithine L-Aspartate |
|
CAS |
3230-94-2 |
|
Molecular Formula |
C9H19N3O6 |
|
Molecular Weight |
265.26 |
|
Storage Details |
2 to 8 °C |
|
Harmonized Tariff Code |
29224985 |
Product Specification
|
Appearance |
White crystalline powder |
|
Assay |
>99% |
|
Specific rotation |
+27 +/-1 |
|
Heavy metals |
<0.001% |
|
pH |
6 - 7 |
|
Loss on Drying |
<7% |
|
Residue on Ignition |
<0.2% |
|
State of Solution |
Clear |
Ornithine aspartate was the first clinically used in the treatment of hangover and hepatic encephalopathy. With the accumulation of clinical application experience, ornithine aspartate has been more widely used in the treatment of liver diseases, and has achieved exact curative effects on hepatic encephalopathy, drug-induced liver damage, fatty liver, chronic hepatitis and other diseases , has been widely recognized by clinicians.
Ornithine aspartate provides a substrate for urea and glutamine synthesis in vivo. Glutamine is the detoxification product of ammonia, as well as the storage and transport form of ammonia. Under physiological and pathological conditions, the synthesis of urea and the synthesis of glutamine are affected by ornithine, aspartic acid and other dicarboxyl compounds. Ornithine is involved in almost the entire process of activation of the urea cycle and detoxification of ammonia. Arginine is formed during this process, and urea is then separated to form ornithine. Aspartic acid participates in the synthesis of nucleic acid in hepatocytes to facilitate the repair of damaged hepatocytes. In addition, due to the indirect promotion of aspartic acid on the metabolic process of tricarboxylic acid cycle in liver cells, it promotes energy synthesis in liver cells, which is conducive to the repair of damaged liver cells and accelerates the recovery of liver function. Recent progress has shown that aspartate can also inhibit the activity of inflammasomes through N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, thereby reducing the pharmacological mechanism of liver inflammatory response. NMDA receptors are a subtype of ionotropic excitatory glutamate receptors, which play an important role in physiological processes such as synaptic transmission, synaptic plasticity, learning and memory in the central nervous system. Subsequent pathological studies also confirmed that aspartate significantly improved inflammatory lesions in the liver.
Clinical application
In the field of liver disease: Ornithine aspartate is widely used as an anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective drug in the treatment of various liver diseases, such as hepatic encephalopathy, drug-induced liver damage, fatty liver, chronic hepatitis, etc. The level of blood ammonia in patients with encephalopathy and the relief of neuropsychiatric symptoms are gradually becoming the main therapeutic drug for the treatment of various liver diseases.
Ornithine aspartate is an essential substrate for the synthesis of urea and glutamine. Ornithine can activate the key enzymes in the process of urea synthesis - ornithine carbamoyltransferase and carbamoyl phosphate synthase, and promote ammonia Metabolism to achieve detoxification of blood ammonia, aspartic acid as a substrate can generate glutamic acid and oxaloacetic acid, glutamine is the detoxification product of ammonia, and it is also the storage and transportation of ammonia. Oxaloacetate participates in the tricarboxylic acid cycle, promotes energy production in liver cells, and enables damaged liver cells to be repaired, regenerated, and restored liver function. Ornithine aspartate can effectively improve liver function, reduce blood ammonia, and synergistically reduce ammonia with lactulose and ofloxacin, thereby significantly improving the cure rate of hepatic encephalopathy, which is worthy of clinical application.
Oncology: With the continuous changes in the types and doses of chemotherapy drugs, complications associated with chemotherapy drugs are also emerging, and liver damage is one of the more common organ damages. Once liver damage occurs, it will affect the physical and mental health of patients to varying degrees, hinder the implementation of chemotherapy regimens, and weaken the therapeutic effect of chemotherapy. In severe cases, liver failure may be life-threatening. Ornithine aspartate can significantly improve liver damage caused by chemotherapy drugs and improve the therapeutic effect of tumor patients.
Surgical operation field: Surgical operation is a blow to the whole body organs of the patient, and postoperative liver function damage is also a common complication. Ornithine aspartate can prevent and treat postoperative liver damage and promote postoperative recovery of patients.