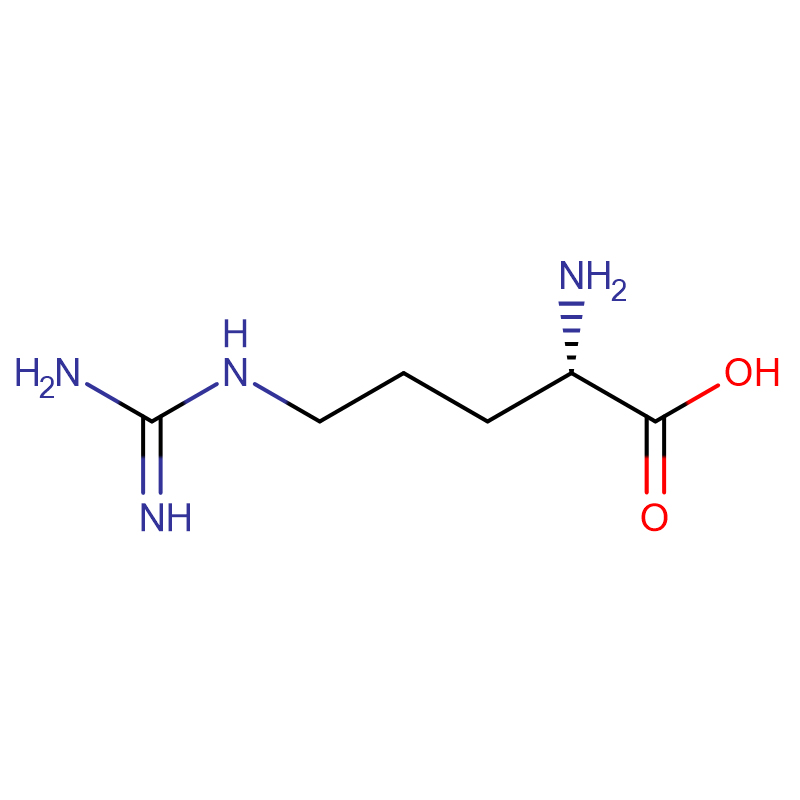
L-Arginine CAS:74-79-3 99% White crystals or crystalline powder
| Catalog Number | XD90323 |
| Product Name | L-Arginine |
| CAS | 74-79-3 |
| Molecular Formula | C6H14N4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 174.20 |
| Storage Details | Ambient |
| Harmonized Tariff Code | 29252900 |
Product Specification
| Appearance | White crystals or crystalline powder |
| Assay | 99% |
| Identification | Infrared Absorption |
| Loss on Drying | ≤ 0.5% |
| Chromatographic purity | Not more than 0.5% of any individual impurity is found ; Not more than 2.0% of total impurities is found |
| Residue on Ignition | ≤ 0.3% |
| Heavy metals ( PB ) | ≤ 0.0015% |
| Iron (as Fe) | ≤ 0.003% |
| Sulfate (as SO4) | ≤ 0.03% |
| Usp grade | USP 33 |
| Chloride (CI) | ≤ 0.05% |
| Specific rotation [ α ] D 2 5 | +26.3 ° ~ +27.7 ° |
The mechanism of Mycobacterium smegmatis G (MbsG), a flavin-dependent l-lysine monooxygenase, was investigated under steady-state and rapid reaction conditions using primary and solvent kinetic isotope effects, substrate analogs, pH and solvent viscosity effects as mechanistic probes. The results suggest that l-lysine binds before NAD(P)H, which leads to a decrease in the rate constant for flavin reduction. l-lysine binding has no effect on the rate of flavin oxidation, which occurs in a one-step process without the observation of a C4a-hydroperoxyflavin intermediate. Similar effects were determined with several substrate analogs. Flavin oxidation is pH independent while the kcat/Km and kred/KD pH profiles for NAD(P)H exhibit single pKa values of ∼6.0, with increasing activity as the pH decreases. At lower pH, the enzyme becomes more uncoupled, producing more hydrogen peroxide and superoxide. Hydride transfer is partially rate-limiting at neutral pH and becomes more rate-limiting at lo w pH. An inverse solvent viscosity effect on kcat/Km for NAD(P)H was observed at neutral pH whereas a normal solvent viscosity effect was observed at lower pH. Together, the results indicate a unique mechanism where a rate-limiting and pH-sensitive conformational change occurs in the reductive half-reaction, which affects the efficiency of lysine hydroxylation.