Factory Free sample Roche - L-Aspartic acid CAS:56-84-8 99% White powder – XD BIOCHEM
Factory Free sample Roche - L-Aspartic acid CAS:56-84-8 99% White powder – XD BIOCHEM Detail:
| Catalog Number | XD90315 |
| Product Name | D-Aspartic acid |
| CAS | 56-84-8 |
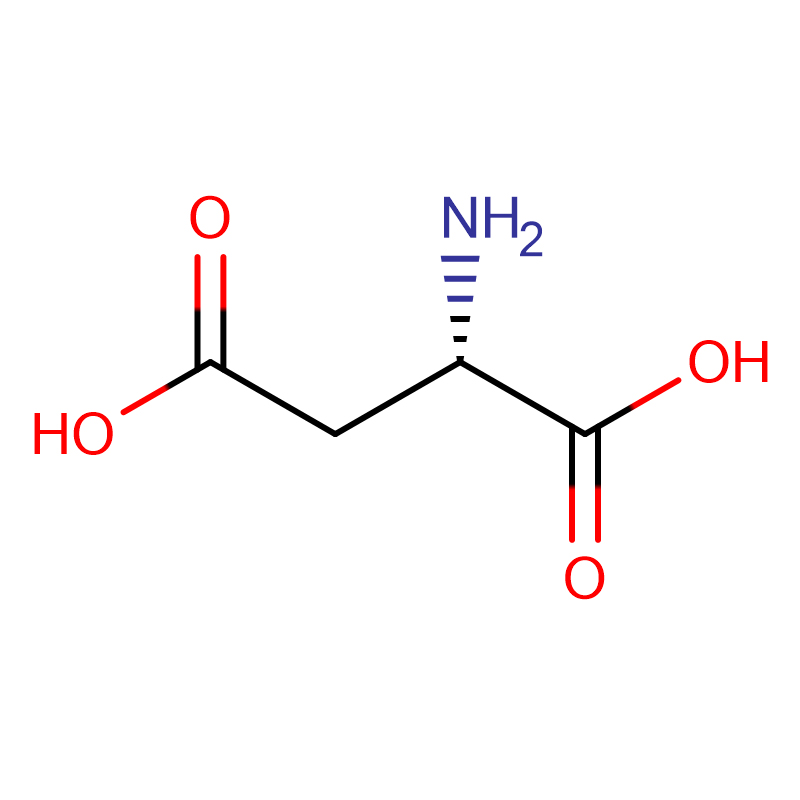
| Molecular Formula | C4H7NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 133.10 |
| Storage Details | 2 to 8 °C |
| Harmonized Tariff Code | 29224985 |
Product Specification
| Appearance | White powder |
| Assay | 99% |
| Grade | USP34 |
| Specific rotation | +24.5 to +26 |
| Lead | <0.0005% |
| Loss on Drying | <0.25% |
| Residue on Ignition | <0.1% |
The EAAT2 glutamate transporter, accounts for >90% of hippocampal glutamate uptake. Although EAAT2 is predominantly expressed in astrocytes, ∼10% of EAAT2 molecules are found in axon terminals. Despite the lower level of EAAT2 expression in glutamatergic terminals, when hippocampal slices are incubated with low concentration of d-aspartate (an EAAT2 substrate), axon terminals accumulate d-aspartate as quickly as astroglia. This implies an unexplained mismatch between the distribution of EAAT2 protein and of EAAT2-mediated transport activity. One hypothesis is that (1) heteroexchange of internal substrate with external substrate is considerably faster than net uptake and (2) terminals favor heteroexchange because of high levels of internal glutamate. However, it is currently unknown whether heteroexchange and uptake have similar or different rates. To address this issue, we used a reconstituted system to compare the relative rates of the two processes in rat and mice. Net uptake was sen sitive to changes in the membrane potential and was stimulated by external permeable anions in agreement with the existence of an uncoupled anion conductance. By using the latter, we also demonstrate that the rate of heteroexchange also depends on the membrane potential. Additionally, our data further suggest the presence of a sodium leak in EAAT2. By incorporating the new findings in our previous model of glutamate uptake by EAAT2, we predict that the voltage sensitivity of exchange is caused by the voltage-dependent third Na(+) binding. Further, both our experiments and simulations suggest that the relative rates of net uptake and heteroexchange are comparable in EAAT2.
Product detail pictures:
Related Product Guide:
Our target should be to consolidate and improve the high-quality and repair of current goods, in the meantime regularly produce new solutions to meet unique customers' needs for Factory Free sample Roche - L-Aspartic acid CAS:56-84-8 99% White powder – XD BIOCHEM , The product will supply to all over the world, such as: Ethiopia, Seattle, Jordan, We also provide OEM service that caters to your specific needs and requirements. With a strong team of experienced engineers in hose design and development, we value every opportunity to provide best products for our customers.
We have been looking for a professional and responsible supplier, and now we find it.