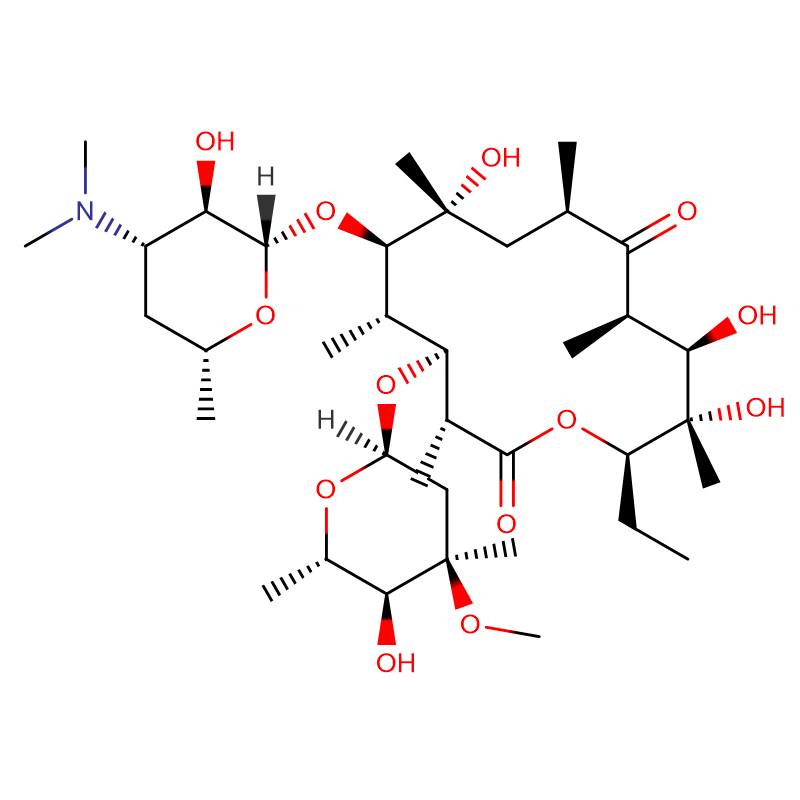
Erythromycin CAS:114-07-8 99% White crystalline powder
| Catalog Number | XD90353 |
| Product Name | Erythromycin |
| CAS | 114-07-8 |
| Molecular Formula | C37H67NO13 |
| Molecular Weight | 733.93 |
| Storage Details | Ambient |
| Harmonized Tariff Code | 29415000 |
Product Specification
| Identification | IR absorption spectrum comparison with USP RS |
| Water | 10% max |
| Ethanol | 0.5% max |
| Residue on Ignition | 0.2% max |
| Assay | 99% |
| Specific rotation | -71 ° to -78 ° |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Crystallinity | Meets the requirements |
| Erythromycin B | 12.0% max |
| Erythromycin C | 5.0% max |
| Limit of thiocyanate | 0.3% max |
| Propanol | 0.5% max |
| N-butyl acetate | 0.5% max |
| Erythromycin A enol ether | 0.3% max |
| Any individual related substastances | 3.0% max |
In the present study, we examined the interaction of antimicrobial agents with four model lipid membranes that mimicked mammalian cell membranes and Gram-positive and -negative bacterial membranes and analyzed the binding kinetics using our surface plasmon resonance (SPR) technique. The selective and specific binding characteristics of antimicrobial agents to the lipid membranes were estimated, and the kinetic parameters were analyzed by application of a two-state reaction model. Reproducible analysis of binding kinetics was observed. Vancomyicn, teicoplanin, erythromycin, and linezolid showed little interaction with the four lipid membranes in the SPR system. On the other hand, vancomycin analogues showed interaction with the model lipid membranes in the SPR system. The selective and specific binding characteristics of vancomycin analogues to the lipid membranes are discussed based on data for in vitro antibacterial activities and our data on the binding affinity of the D-alanyl-D-ala nine terminus of a pentapeptide cell wall obtained by SPR. The mechanism of antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin-resistant enterococci could be evaluated using the binding affinity obtained with our SPR techniques. The results indicate that the SPR method could be widely applied to predict binding characteristics, such as selectivity and specificity, of many antimicrobial agents to lipid membranes.