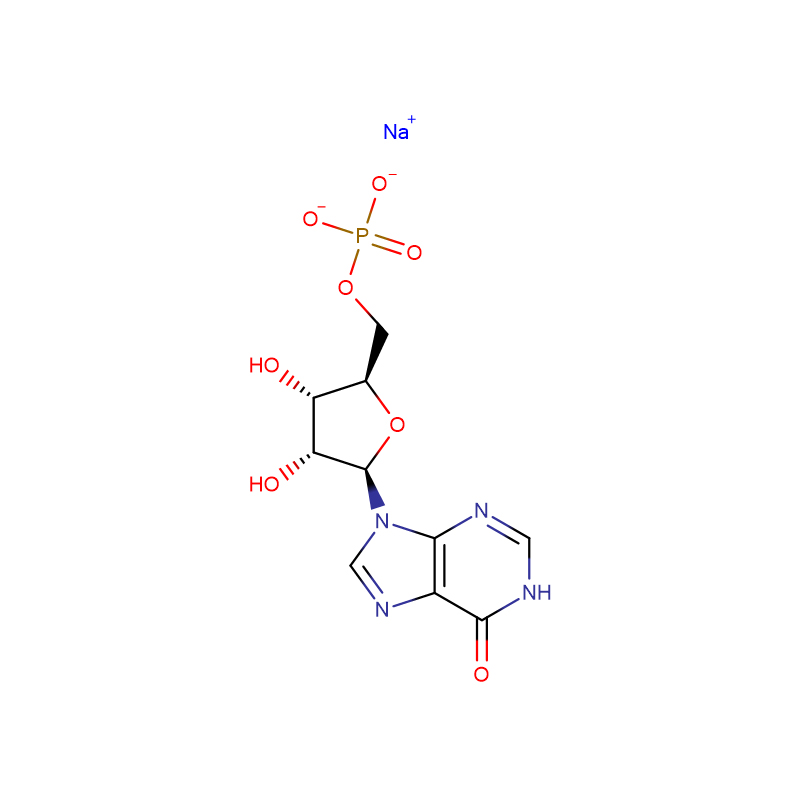
Disodium 5′-Inosinate Cas:4691-65-0 White or off-white crystalline powder
| Catalog Number | XD90175 |
| Product Name | Disodium 5'-Inosinate |
| CAS | 4691-65-0 |
| Molecular Formula | C10H11N4Na2O8P |
| Molecular Weight | 392.16 |
| Storage Details | Ambient |
| Harmonized Tariff Code | 2103909000 |
Product Specification
| Appearance | White or off-white crystalline powder |
| Assay | 99% |
| Melting point | 175 ºC |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Solubility | Slightly hygroscopic, easily soluble in water (20℃, 13g/100mL), slightly soluble in ethanol and ether. The pH value of a 5% aqueous solution is 7.0 to 8.5. |
Properties: Disodium inosinate is colorless to white crystals, or white crystalline powder, containing about 7.5 molecules of crystal water, not hygroscopic. It starts to lose crystal water at 40°C, and becomes anhydrous above 120°C. Xian, the umami threshold is 0.025g/100mL, and the umami intensity is lower than that of sodium guanylate, but the combination of the two has a significant synergistic effect. When the two are mixed 1:1, the umami threshold can be reduced to 0.0063%. Combined with 0.8% sodium glutamate, the umami threshold is further reduced to 0.000031%. Soluble in water, the aqueous solution is stable and neutral. It is easily decomposed when heated in an acidic solution and loses its taste. It can also be broken down by phosphatase. Slightly soluble in ethanol, almost insoluble in ether.
Chemical Properties: Colorless to white crystals, or white crystalline powder. It contains an average of 7.5 molecules of crystal water. Odorless, with a special taste. Taste threshold 0.012%. Not deliquescence. The melting point is not obvious, it is brown at 180°C, and decomposes at about 230°C. Stable, no decomposition under normal food processing conditions (Ph value 4 to 7) and heating at 100°C for 1 hour. It has a synergistic effect on umami taste with sodium L-glutamate (for example, if the ratio of sodium inosinate to sodium L-glutamate is 1:7, it will obviously enhance the umami taste). The maximum absorption wavelength of its hydrochloric acid solution is 250nm±2nm. In case of phosphatase in animals and plants, it can be decomposed and lose its umami. It starts to lose crystal water at 44°C, and becomes anhydrous above 120°C. Easily soluble in water (13g/100ml, 20℃), the aqueous solution is neutral, slightly soluble in ethanol, almost insoluble in ether.
Use limit GB 2760-96: all kinds of food, limited to GMP FAO/WHO (1994): luncheon meat, ham, bacon and other meats
Uses: Disodium inosinate as flavor enhancer, nutritional additive
purposes : umami agent. Such as adding 50,000 to 100,000th of soy sauce, that is, a special umami. Generally, it is used in combination with monosodium glutamate, sodium guanylate, etc. to improve the freshness-enhancing effect.
Uses: Sodium inosinate is a flavoring agent that is allowed to be used at home and abroad. It is rarely used alone. It is often mixed with monosodium glutamate. When mixed, the umami taste has a synergistic effect. my country stipulates that it can be used for all kinds of feed and food additives, and can be used in moderation according to production needs.
Uses: Sodium inosinate is also a flavoring agent that is allowed to be used at home and abroad. It is rarely used alone. It is often mixed with monosodium glutamate. When mixed, the umami taste has a synergistic effect. Our country stipulates that it can be used for all kinds of food, and it can be used in moderation according to production needs.
Uses: Mainly used for leukopenia and acute and chronic liver diseases caused by various reasons.