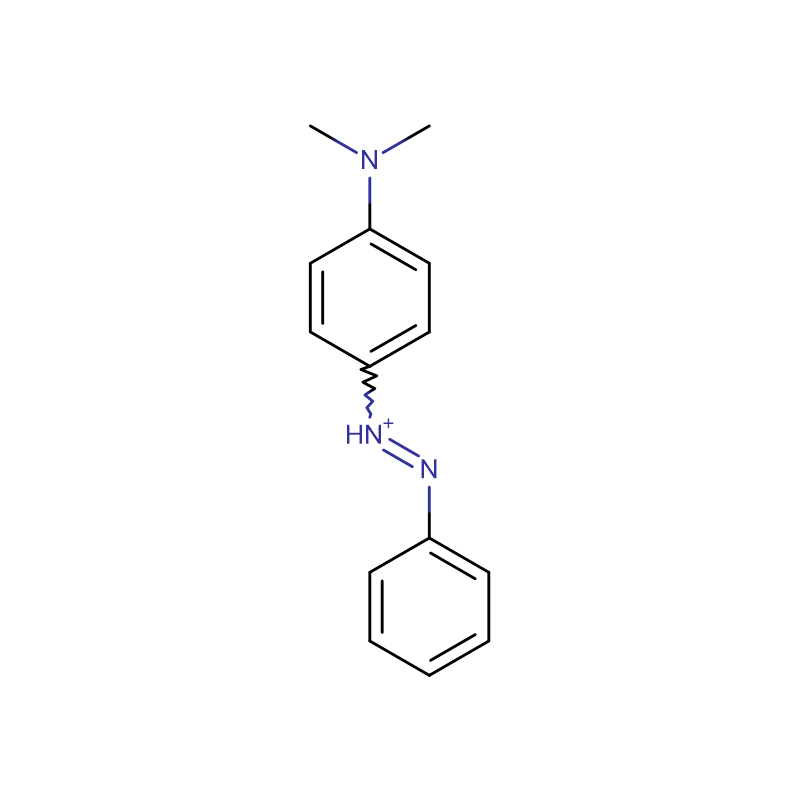
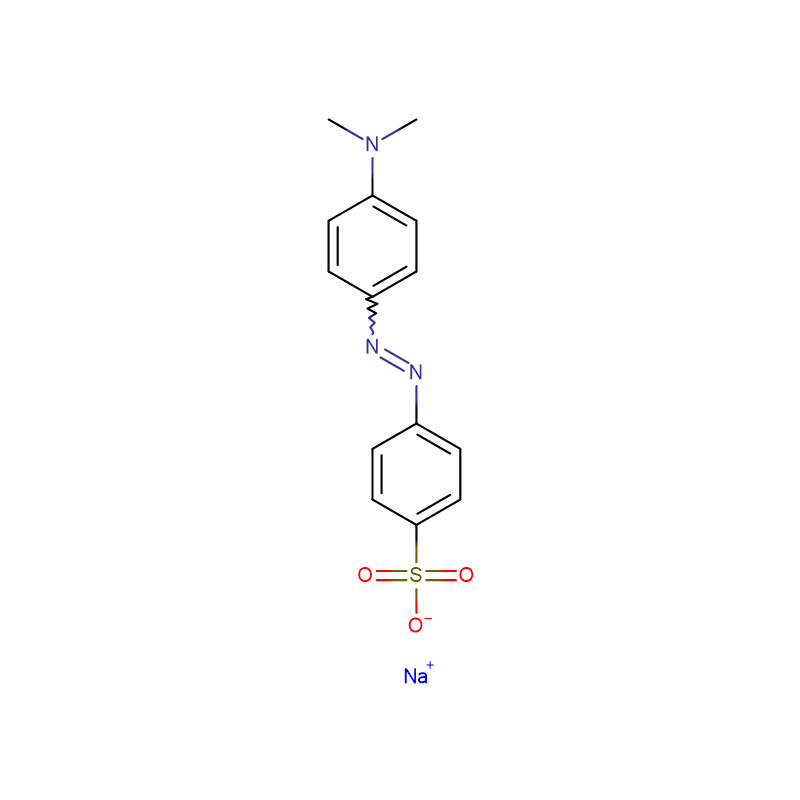
Dimethyl yellow CAS:60-11-7 Yellow to Orange to brown powder
| Catalog Number | XD90467 |
| Product Name | Dimethyl yellow |
| CAS | 60-11-7 |
| Molecular Formula | C14H15N3 |
| Molecular Weight | 225-29 |
| Storage Details | Ambient |
| Harmonized Tariff Code | 29270000 |
Product Specification
| Melting Point | 105-116 Deg C |
| Appearance | Yellow to Orange to brown powder |
| Assay | 99% |
| Loss on Drying | <1.0% |
| Strength | 98.67% |
| Colour Change | Red @ pH 2.9, Yellow @ pH 4.9 |
| Sulfated ash | 0.4% |
| Lamda Max | 400nm (in methanol) |
The membrane topology of the colicin E1 channel domain was studied by fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET). The FRET involved a genetically encoded fluorescent amino acid (coumarin) as the donor and a selectively labeled cysteine residue tethered with DABMI (4-(dimethylamino)phenylazophenyl-4'-maleimide) as the FRET acceptor. The fluorescent coumarin residue was incorporated into the protein via an orthogonal tRNA/aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase pair that allowed selective incorporation into any site within the colicin channel domain. Each variant harbored a stop (TAG) mutation for coumarin incorporation and a cysteine (TGT) mutation for DABMI attachment. Six interhelical distances within helices 1-6 were determined using FRET analysis for both the soluble and membrane-bound states. The FRET data showed large changes in the interhelical distances among helices 3-6 upon membrane association providing new insight into the membrane-bound structure of the channel domain. In general, the coumarin-DABMI FRET interhelical efficiencies decreased upon membrane binding, building upon the umbrella model for the colicin channel. A tentative model for the closed state of the channel domain was developed based on current and previously published FRET data. The model suggests circular arrangement of helices 1-7 in a clockwise direction from the extracellular side and membrane interfacial association of helices 1, 6, 7, and 10 around the central transmembrane hairpin formed by helices 8 and 9.