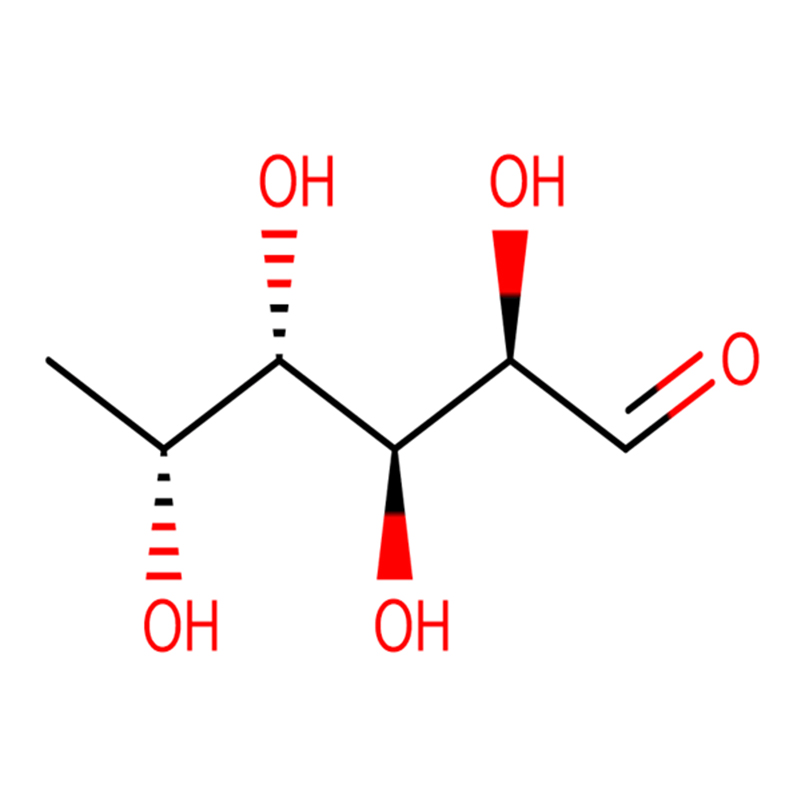
D-(+)-FUCOSE CAS:3615-37-0 98% White To Off-White Crystalline Powder
| Catalog Number | XD90009 |
| Product Name | D-(+)-FUCOSE |
| CAS | 3615-37-0 |
| Molecular Formula | C6H12O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 164.16 |
| Storage Details | 2 to 8 °C |
| Harmonized Tariff Code | 29400000 |
Product Specification
| Physical Appearance | White to off-white crystalline powder |
| Purity (HPLC) | min 98% |
| Identification | 1H NMR in D2O: Conforms to structure |
| Storage Temperature | +20 ° C |
| Molecular Weight | 164.16 |
| Solubility | 5% water solution: Clear, colourless to very pale yellow |
| Specific optical rotation | a 20 (c=2, H O, 24h): +74 to +78° |
| Water Content (KF) | max 0.5% |
Application of D-(+)-FUCOSE
The vast majority of fucose in nature is L-fucose, and D-fucose in D configuration is only a rare sugar and is found in some glycosides.
D-Fucose D-Fucose >98%. A kind of six-carbon sugar, which can be regarded as a methyl pentose. L-fucose is present in seaweed and gums in large quantities, and is also found in the polysaccharides of some bacteria.
As a component of sugar chains in glycoproteins, fucose is widely present on the plasma membrane of various cell surfaces. Fucose has one less hydroxyl group on the sixth carbon atom than general six-carbon sugars, so fucose is less hydrophilic and more hydrophobic than other monosaccharides. Fucose in certain blood group molecules is a marker of a certain blood group.
Glycans (N-linked glycans) present on the surface of mammalian, plant cells and insects. Fucose monomers can polymerize to form fucoidan. L-fucose is the only universal form in nature, and D-fucose is a synthetic analogue of galactose.
Two features distinguish fucose from other six-carbon sugars present in mammals, namely the lack of a hydroxyl group on carbon six and its L configuration.
A type of six-carbon sugar. And can be seen as a methyl pentose. The vast majority of fucose existing in nature is L-fucose, and fucose with D configuration is only a rare sugar and is found in some glycosides. L-fucose is present in large amounts in seaweed and gums, and is also found in the polysaccharides of certain bacteria. As a component of sugar chains in glycoproteins, fucose is widely present on the plasma membrane of various cell surfaces. Fucose has one less hydroxyl group on the sixth carbon atom than general six-carbon sugars, so fucose is less hydrophilic and more hydrophobic than other monosaccharides. Fucose in certain blood group molecules is a marker of a certain blood group. Usually, fucose is extracted from seaweed, first treated with acid, neutralized, and then precipitated in the form of phenylhydrazone, and phenylhydrazine is removed to obtain α-L-fucose crystals.