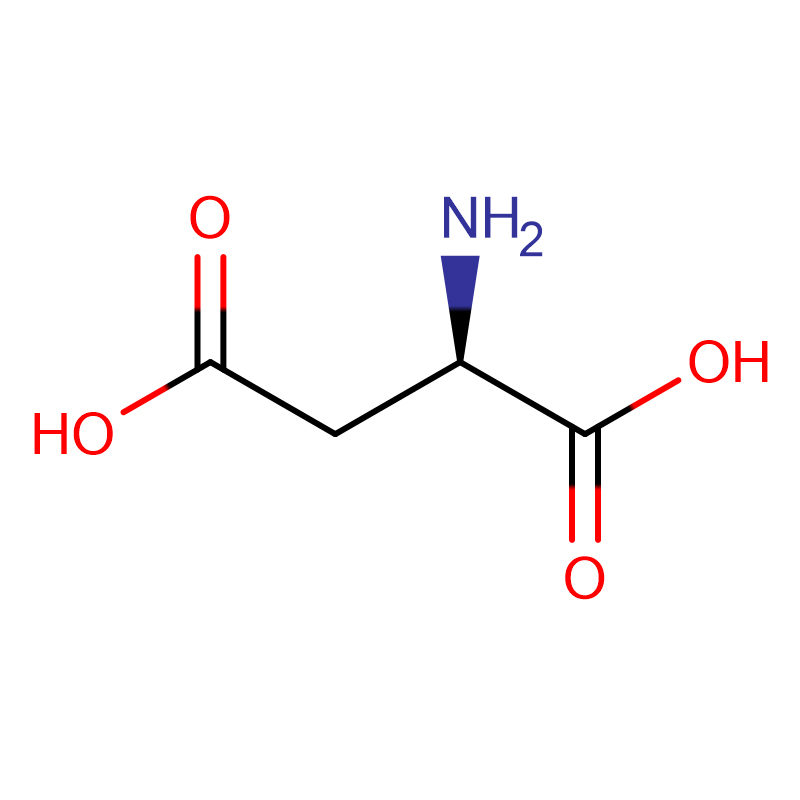
D-Aspartic acid CAS:1783-96-6 99% White powder
| Catalog Number | XD90316 |
| Product Name | D-Aspartic acid |
| CAS | 1783-96-6 |
| Molecular Formula | C4H7NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 133.10 |
| Storage Details | Ambient |
| Harmonized Tariff Code | 29224985 |
Product Specification
| Appearance | White powder |
| Assay | 99% |
| Specific rotation | -24 to -26 |
| Heavy metals | <10ppm |
| AS | <1ppm |
| pH | ≤0.2% |
| SO4 | <0.02% |
| Fe | <10ppm |
| Loss on Drying | <0.20% |
| Residue on Ignition | <0.10% |
| NH4 | <0.02% |
| Transmittance | >98% |
| Cl | <0.02% |
Secondary transporters are integral membrane proteins that catalyse the movement of substrate molecules across the lipid bilayer by coupling substrate transport to one or more ion gradients, thereby providing a mechanism for the concentrative uptake of substrates. Here we describe crystallographic and thermodynamic studies of Glt(Ph), a sodium (Na+)-coupled aspartate transporter, defining sites for aspartate, two sodium ions and d,l-threo-beta-benzyloxyaspartate, an inhibitor. We further show that helical hairpin 2 is the extracellular gate that controls access of substrate and ions to the internal binding sites. At least two sodium ions bind in close proximity to the substrate and these sodium-binding sites, together with the sodium-binding sites in another sodium-coupled transporter, LeuT, define an unwound alpha-helix as the central element of the ion-binding motif, a motif well suited to the binding of sodium and to participation in conformational changes that accompany ion binding and unbinding during the transport cycle.