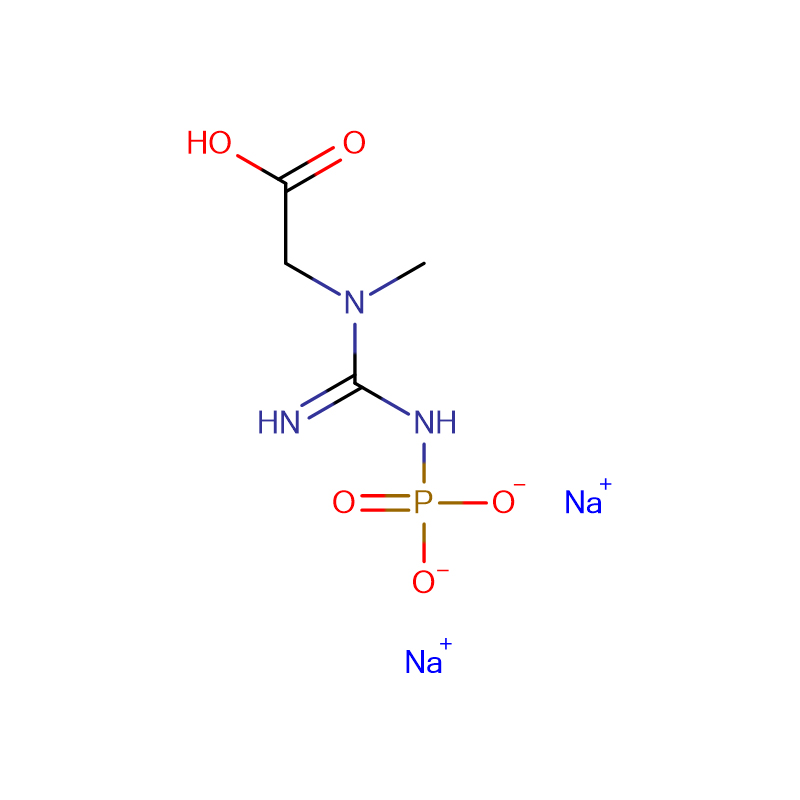
Creatine phosphate disodium salt Cas:922-32-7 98% Yellow powder
| Catalog Number | XD90171 |
| Product Name | Creatine phosphate disodium salt |
| CAS | 922-32-7 |
| Molecular Formula | C4H8N3Na2O5P · 4H2O |
| Molecular Weight | 327.14 |
| Storage Details | Ambient |
| Harmonized Tariff Code | 29299000 |
Product Specification
| Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Assay | >98.0% min |
| Water | <0.5% |
| Heavy metals | <5ppm |
Cardioprotectant: Creatine phosphate is an important energy-supplying substance in muscle contraction and metabolism. It is the chemical energy reserve of smooth muscle and striated muscle, and is used for ATP resynthesis. Phosphocreatinedisodium is its medicinal form. Sodium Creatine Phosphate, chemical name N-[imino(phosphono)methyl]-N-methylglycine disodium salt, is a cardioprotective agent launched by Italian Ouhui Pharmaceutical Factory in 1992. The phosphocreatine form plays a variety of important physiological roles, and is widely used for myocardial protection in patients with cardiac ischemia or during cardiac Chemicalbook surgery, and for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases such as heart failure, myocardial infarction and arrhythmia. It can improve cardiac function and heart rate variability in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy. It can not only provide energy for myocardial cells when they suffer from ischemia and hypoxia, but also protect myocardial cell membranes from the invasion of oxygen free radicals and other harmful substances, which can affect cardiac function. Postoperative myocardial protection in patients with incompetent valvular disease is beneficial to postoperative recovery of cardiac function in patients with incompetent valvular disease. Using it to comprehensively treat myocardial damage after neonatal asphyxia can significantly improve myocardial enzymes and electrocardiogram, and has good curative effect and safety.
Function characteristics This product is the chemical energy reserve of cardiac and skeletal muscles, and is used for the resynthesis of ATP, providing energy for the process of actomyosin contraction, and plays an important role in the energy metabolism of muscle contraction. Insufficient energy supply is an important factor in the formation and development of myocardial cell injury.
1. It has a significant protective effect on ischemic myocardial systolic function, which can fully restore contractility and rapidly decrease diastolic blood pressure.
2. Maintain the content of adenosine triphosphate and creatine phosphate in cells, and Chemicalbook maintains the myocardial energy reserve.
3. Reduce the loss of creatine kinase and reduce the damage of cell membrane.
4. It has anti-peroxidation properties.
5. Improve myocardial microcirculation. Due to the existence of high-energy phosphate bonds in creatine phosphate molecules, the high-energy phosphate bonds can directly convert ADP into ATP under the action of creatine phosphate, and directly give energy to the body to act immediately. As an intermediate product of glycolysis, sodium fructose diphosphate needs to play an indirect role through anaerobic metabolism.
synthetic route:
1 Using dibenzyl phosphate as raw material, react with oxalyl chloride to obtain dibenzyl oxyphosphoryl chloride,
2 Under the action of triethylamine, the dibenzyloxyphosphoryl creatine ethyl ester obtained by the reaction with creatine ethyl ester hydrochloride is cyclized to dibenzyloxyphosphoryl creatinine,
3. After palladium carbon catalyzed hydrogenolysis to debenzylate, react with sodium hydroxide to obtain disodium creatinine phosphate,
4 is hydrolyzed to 1 under the action of sodium hydroxide.
Uses: It is suitable for protecting the abnormal myocardial metabolism in the state of myocardial ischemia.
Adverse reactions, contraindications and drug effects: those who are allergic to the components of this product are prohibited; those with chronic renal insufficiency are prohibited from using large doses (5-10g/d). Rapid intravenous injection of more than 1g can cause a decrease in blood pressure. High-dose administration results in high phosphate intake, which can affect calcium metabolism and secretion of hormones that regulate homeostasis, affecting renal function and purine metabolism.