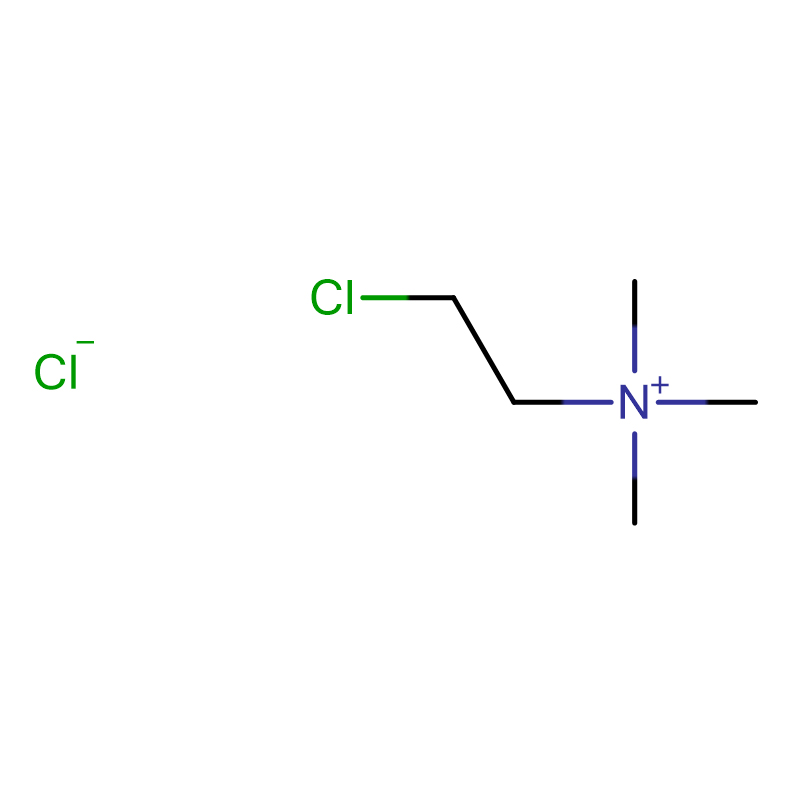
Chlormequat chloride Cas:999-81-5
| Catalog Number | XD91939 |
| Product Name | Chlormequat chloride |
| CAS | 999-81-5 |
| Molecular Formula | C5H13Cl2N |
| Molecular Weight | 158.07 |
| Storage Details | Ambient |
Product Specification
| Appearance | White powder |
| Assay | 99% min |
| Melting point | 239-243 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Boiling point | 260.3°C (rough estimate) |
| density | 1.2228 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5500 (estimate) |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Corrodes many metals. Very hygroscopic. |
Function
Ethephon often used on wheat, coffee, tobacco, cotton, and rice in order to help the plant's fruit reach ripeness more quickly.
Cotton is the most important single crop use for ethephon. It initiates fruiting over a period of several weeks, promotes early concentrated boll opening, and enhances defoliation to facilitate and improve efficiency of scheduled harvesting. Harvested cotton quality is improved.
Ethephon also is widely used by pineapple growers to initiate reproductive development (force) of pineapple. Ethephon is also sprayed on mature-green pineapple fruits to degreen them to meet produce marketing requirements. There can be some detrimental effect on fruit quality.
Although many environmental groups worry about toxicity resulting from use of growth hormones and fertilizers, the toxicity of ethephon is actually very low,[2] and any ethephon used on the plant is converted very quickly to ethylene.
Application
a) To accelerate ripening of fruit, tomatoes, sugar beet, coffee, etc.
b) To increase the tillering of wheat and rice
c) To prevent lodging in rice, maize and flax
d) To accelerate boll opening and defoliation in cotton
e) To hasten the yellowing of mature tobacco leaves
f) To stimulate latex flow in rubber trees, and resin flow in pine trees
g) To stimulate early uniform hull split in walnuts, etc.