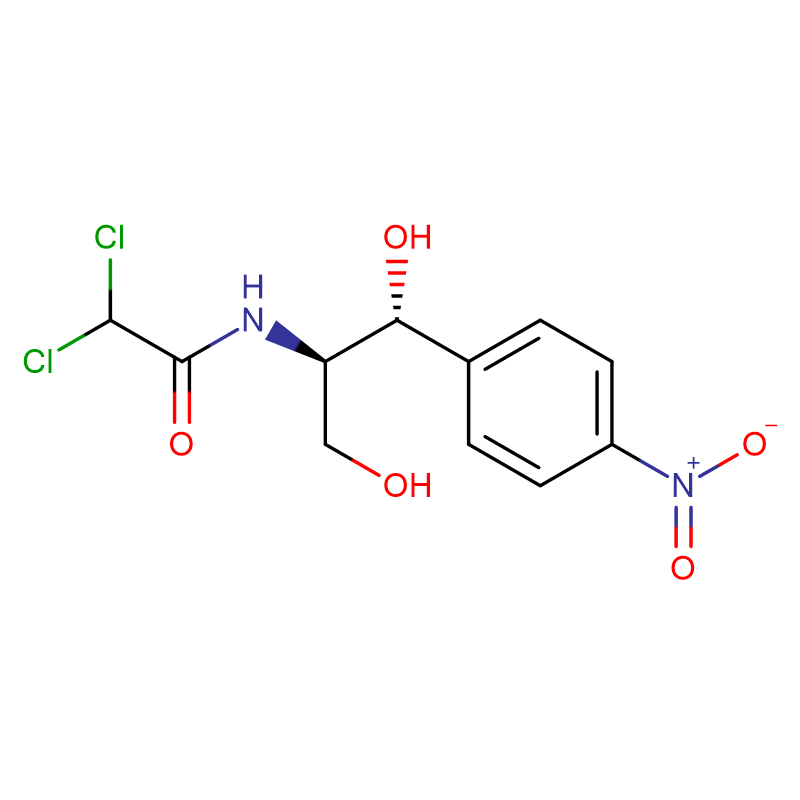
Chloramphenicol CAS:56-75-7 99% White powder
| Catalog Number | XD90355 |
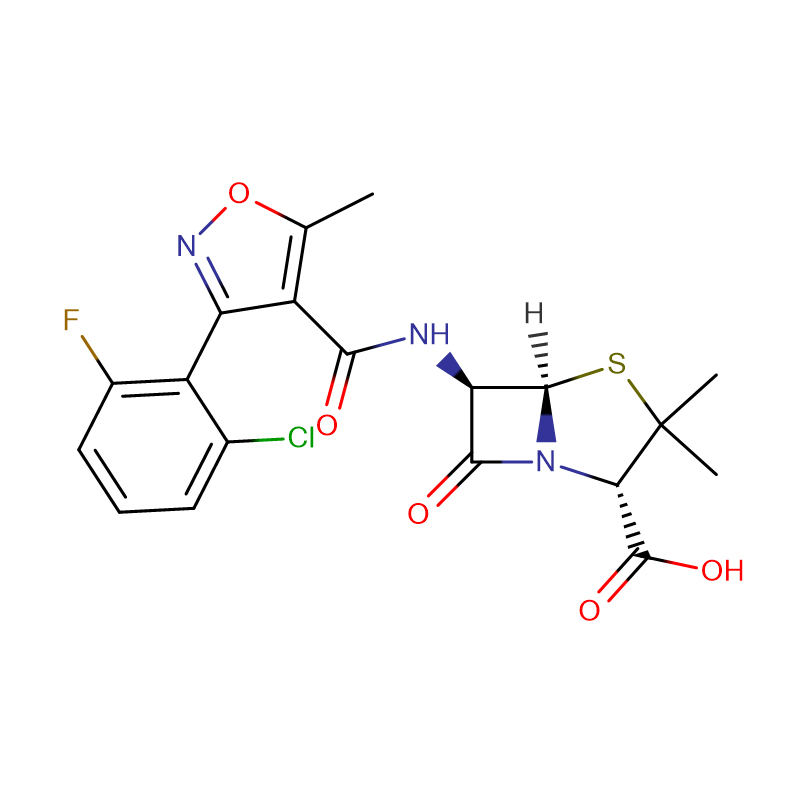
| Product Name | Chloramphenicol |
| CAS | 56-75-7 |
| Molecular Formula | C11H12Cl2N2O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 323.13 |
| Storage Details | Ambient |
| Harmonized Tariff Code | 29414000 |
Product Specification
| Melting Point | 149.0°C - 153.0°C |
| pH | 4.5-7.5 |
| Assay | 99% |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Heavy metals | <20ppm |
| Loss on Drying | 0.5% max |
| Residue on Ignition | <0.10% |
The brucellae are the etiological agents of brucellosis, a worldwide-distributed zoonosis. These bacteria are facultative intracellular parasites and thus are able to adjust their metabolism to the extra- and intracellular environments encountered during an infectious cycle. However, this aspect of Brucella biology is imperfectly understood, and the nutrients available in the intracellular niche are unknown. Here, we investigated the central pathways of C metabolism used by Brucella abortus by deleting the putative fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (fbp and glpX), phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (pckA), pyruvate phosphate dikinase (ppdK), and malic enzyme (mae) genes. In gluconeogenic but not in rich media, growth of ΔppdK and Δmae mutants was severely impaired and growth of the double Δfbp-ΔglpX mutant was reduced. In macrophages, only the ΔppdK and Δmae mutants showed reduced multiplication, and studies with the ΔppdK mutant confirmed that it reached the replicative niche. Similarly, onl y the ΔppdK and Δmae mutants were attenuated in mice, the former being cleared by week 10 and the latter persisting longer than 12 weeks. We also investigated the glyoxylate cycle. Although aceA (isocitrate lyase) promoter activity was enhanced in rich medium, aceA disruption had no effect in vitro or on multiplication in macrophages or mouse spleens. The results suggest that B. abortus grows intracellularly using a limited supply of 6-C (and 5-C) sugars that is compensated by glutamate and possibly other amino acids entering the Krebs cycle without a critical role of the glyoxylate shunt.