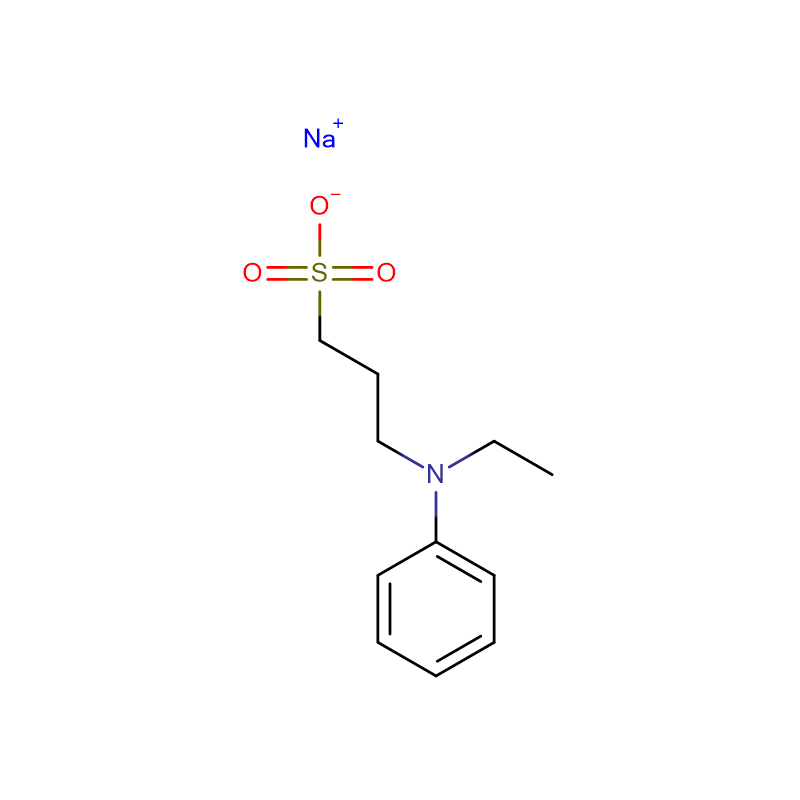
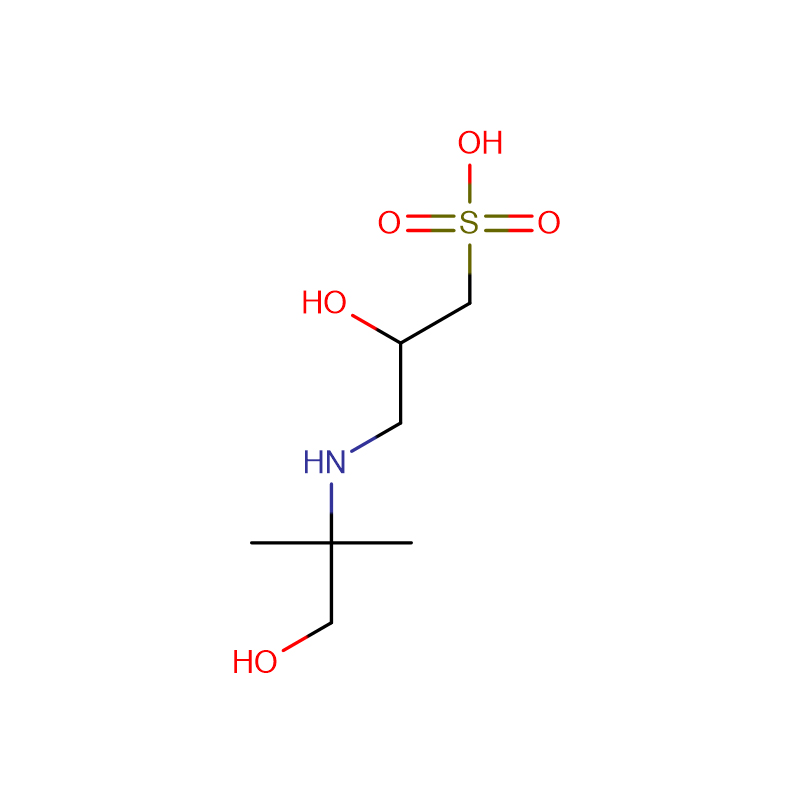
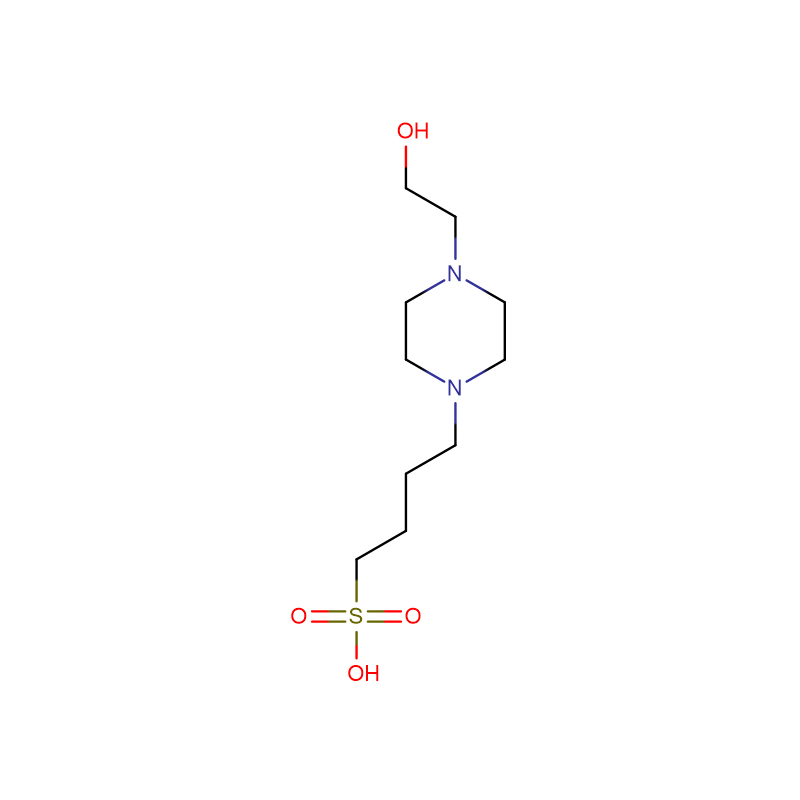
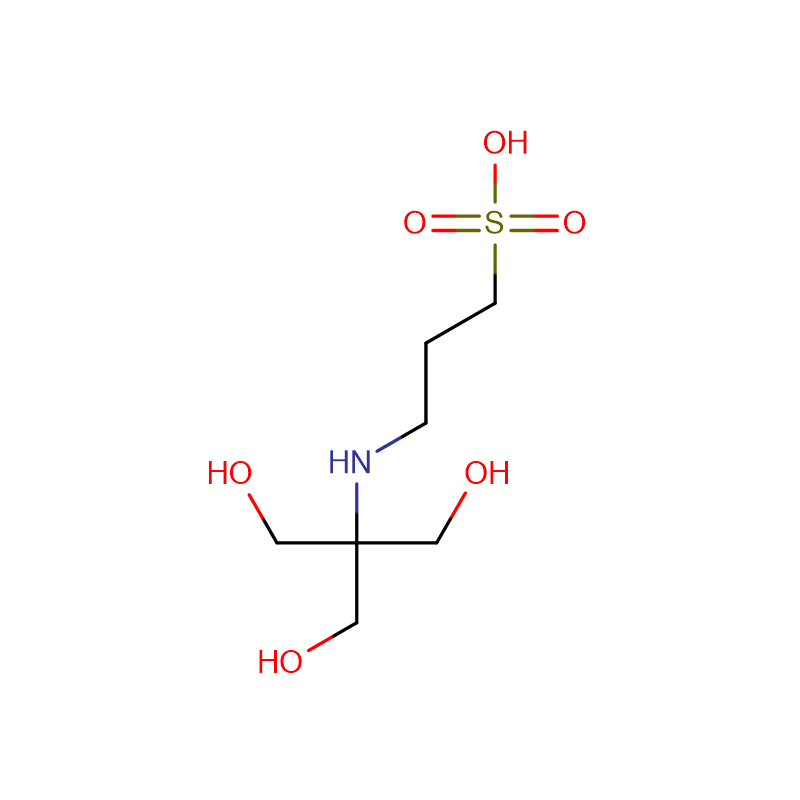
The new Trinder's reagent is a highly water-soluble aniline derivative that is widely used in diagnostic assays and biochemical tests. It has several advantages over conventional chromogenic reagents in the colorimetric determination of hydrogen peroxide activity. The new Trinder's reagent is sufficiently stable to both It can be used in solution or in test pipeline detection system. In the presence of hydrogen peroxide and peroxidase, the new Trinder'si reagent can be used in combination with 4-aminoantipyrine (4-AA) or 3 methyl During the oxidative coupling reaction of benzothiazole sulfonehydrazone (MBTH), very stable purple or blue dyes are formed. The molar absorbance of the dyes coupled with MBTH is 1.5-2 times higher than that of the dyes coupled with 4-AA; however, 4-AA The solution is more stable than MBTH solution. The substrate is enzymatically oxidized by its oxidase to generate hydrogen peroxide. The concentration of this hydrogen peroxide corresponds to the concentration of the substrate. Therefore, the amount of the substrate can be determined by the color development of the oxidative coupling reaction. Glucose , alcohol, acyl-CoA, and cholesterol can be used to detect those substrates coupled with novel Trinder's reagents and 4-AA. There are 10 new Trinder's reagents. Among the new Trinder's reagents, TOOS is the most commonly used. However, for a specific substrate, testing different kinds of novel Trinder's reagents is necessary to develop the optimal detection system.