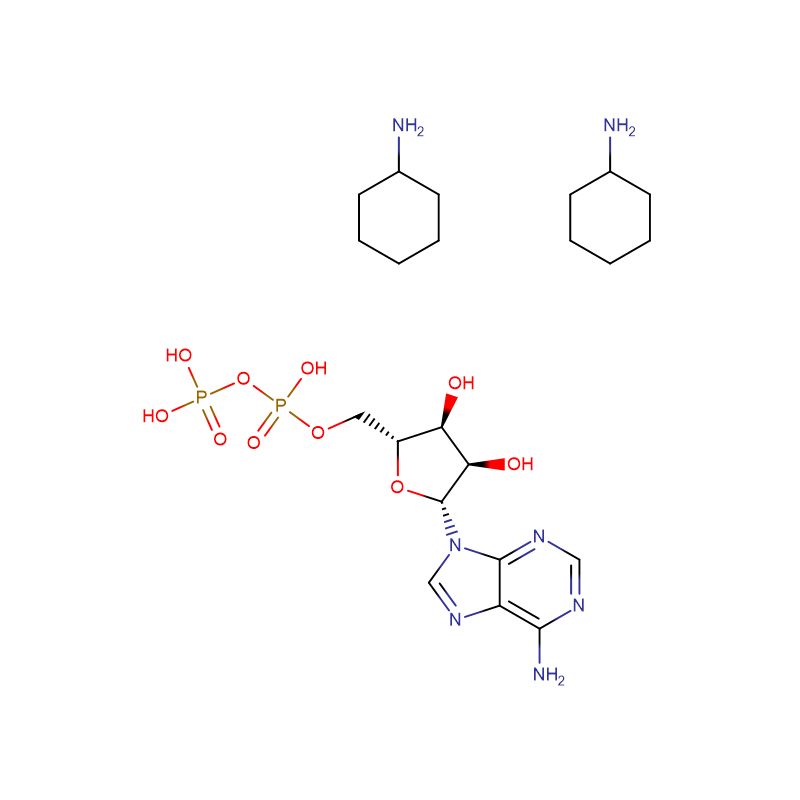
adenosine 5′-diphosphate di(monocyclohexylammoniu Cas: 102029-87-8 99% White powder
| Catalog Number | XD90159 |
| Product Name | adenosine 5'-diphosphate di(monocyclohexylammoniu |
| CAS | 102029-87-8 |
| Molecular Formula | C10H15N5O10P2·2C6H13N |
| Molecular Weight | 625.55 |
| Storage Details | 2 to 8 °C |
| Harmonized Tariff Code |
Product Specification
| Appearance | White powder |
| Assay | 99% |
1.To investigate whether adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-derived adenosine might inhibit platelet aggregation, especially in the presence of a P2Y₁₂ antagonist, where the effects of ADP at the P2Y₁₂ receptor would be prevented.Platelet aggregation was measured in response to thrombin receptor activator peptide by platelet counting in platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and whole blood in the presence of ADP and the P2Y₁₂ antagonists cangrelor, prasugrel active metabolite, and ticagrelor. In the presence of a P2Y₁₂ antagonist, preincubation of PRP with ADP inhibited aggregation; this effect was abolished by adenosine deaminase. No inhibition of aggregation occurred in whole blood except when dipyridamole was added to inhibit adenosine uptake into erythrocytes. The effects of ADP in PRP and whole blood were replicated using adenosine and were directly related to changes in cAMP (assessed by vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein phosphorylation). All results were the same irrespective of the P2Y₁₂ ant agonist used.ADP inhibits platelet aggregation in the presence of a P2Y₁₂ antagonist through conversion to adenosine. Inhibition occurs in PRP but not in whole blood except when adenosine uptake is inhibited. None of the P2Y₁₂ antagonists studied replicated the effects of dipyridamole in the experiments that were performed.
2.ADP is considered a weak platelet agonist due to the limited aggregation responses it induces in vitro at physiological concentrations of extracellular Ca(2+) [(Ca(2+) )(o) ]. Lowering [Ca(2+) ](o) paradoxically enhances ADP-evoked aggregation, an effect that has been attributed to enhanced thromboxane A(2) production. This study examined the role of ectonucleotidases in the [Ca(2+) ](o) -dependence of platelet activation. Reducing [Ca(2+) ](o) from millimolar to micromolar levels converted ADP (10 μmol/l)-evoked platelet aggregation from a transient to a sustained response in both platelet-rich plasma and washed suspensions. Blocking thromboxane A(2) production with aspirin had no effect on this [Ca(2+) ](o) -dependence. Prevention of ADP degradation abolished the differences between low and physiological [Ca(2+) ](o) resulting in a robust and sustained aggregation in both conditions. Measurements of extracellular ADP revealed reduced degradation in both plasma and apyrase-containin g saline at micromolar compared to millimolar [Ca(2+) ](o) . As reported previously, thromboxane A(2) generation was enhanced at low [Ca(2+) ](o) , however this was independent of ectonucleotidase activity(.) P2Y receptor antagonists cangrelor and MRS2179 demonstrated the necessity of P2Y(12) receptors for sustained ADP-evoked aggregation, with a minor role for P2Y(1) . In conclusion, Ca(2+) -dependent ectonucleotidase activity is a major factor determining the extent of platelet aggregation to ADP and must be controlled for in studies of P2Y receptor activation.