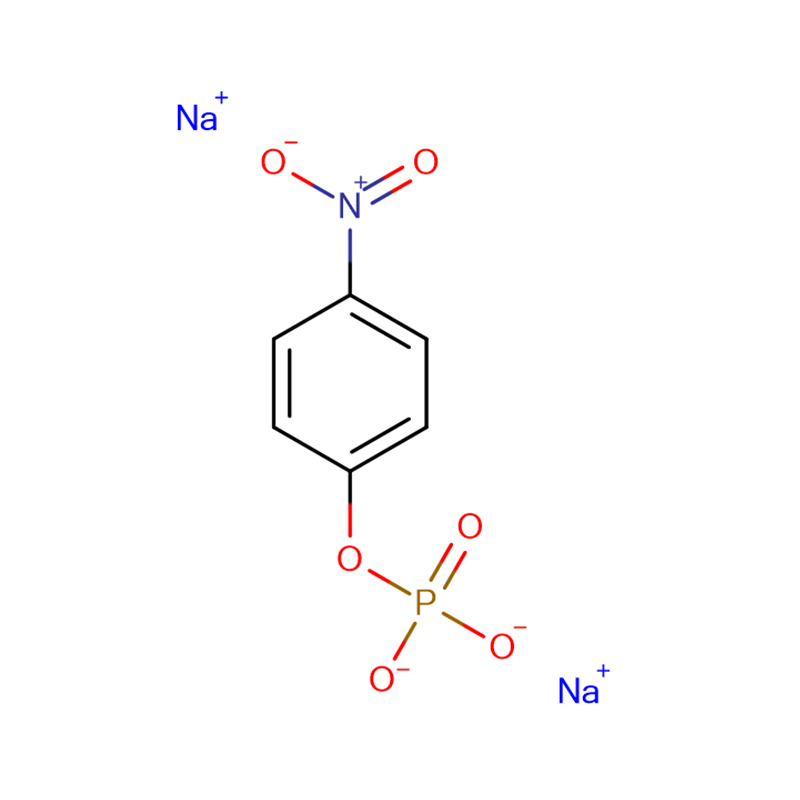
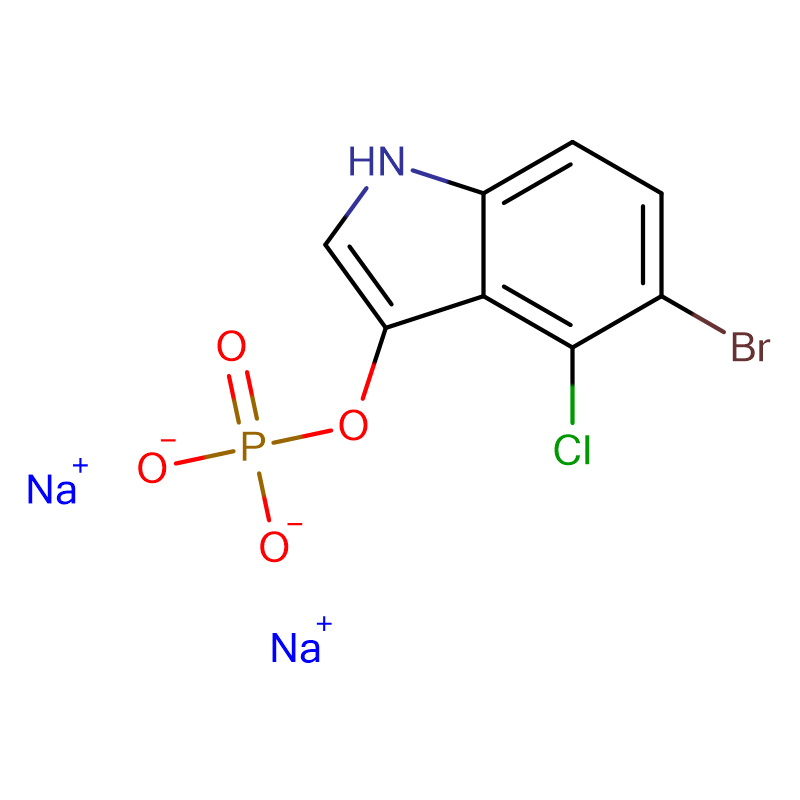
5-Bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate disodium salt Cas:102185-33-1 White to off-white with light cream tinge crystalline powder
| Catalog Number | XD90135 |
| Product Name | 5-Bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate disodium salt |
| CAS | 102185-33-1 |
| Molecular Formula | C8H4BrClNO4Na2P |
| Molecular Weight | 370.43 |
| Storage Details | -15 to -20 °C |
| Harmonized Tariff Code | 29339980 |
Product Specification
| Appearance | White to off-white with light cream tinge crystalline powder |
| Assay | 99% |
| Solubility | Clear and colorless solution ( Sol. 2%, water) |
| TLC | 100% |
| H-NMR Spectrum | Conforming to structure |
| Water | ≤ 10.0% |
The lung is a branched tubular network with two distinct compartments--the proximal conducting airways and the peripheral gas exchange region--separated by a discrete boundary termed the bronchoalveolar duct junction (BADJ). Here we image the developing mouse lung in three-dimensions (3D) and show that two nested developmental waves demarcate the BADJ under the control of a global hormonal signal. A first wave of branching morphogenesis progresses throughout embryonic development, generating branches for both compartments. A second wave of conducting airway differentiation follows the first wave but terminates earlier, specifying the proximal compartment and setting the BADJ. The second wave is terminated by a glucocorticoid signalling: premature activation or loss of glucocorticoid signalling causes a proximal or distal shift, respectively, in BADJ location. The results demonstrate a new mechanism of boundary formation in complex, 3D organs and provide new insights into glucocorticoid therapies for lung defects in premature birth.


![1,2,3,4-Tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinolin-3-ol CAS:5423-67-6 Off-white powder](https://cdn.globalso.com/xdbiochems/5423-67-6.jpg)