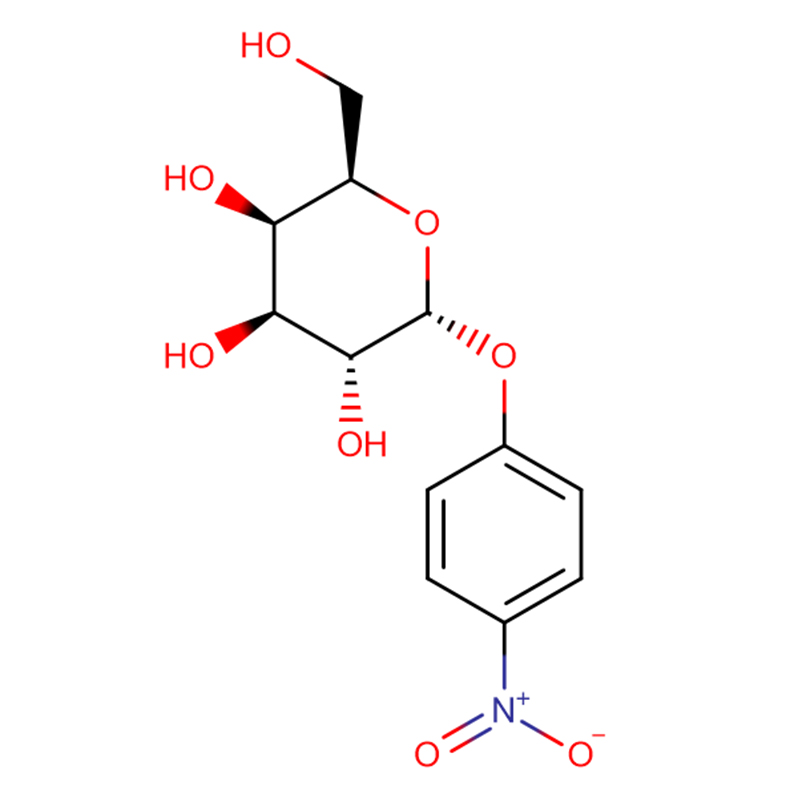
4-Nitrophenyl-alpha-D-galactopyranoside CAS:7493-95-0 99%
| Catalog Number | XD900018 |
| Product Name | 4-Nitrophenyl-alpha-D-galactopyranoside |
| CAS | 7493-95-0 |
| Molecular Formula | C12H15NO8 |
| Molecular Weight | 301.25 |
| Storage Details | -15 to -20 °C |
| Harmonized Tariff Code | 29400000 |
Product Specification
| Appearance | White to Orange to Green powder to crystal |
| Assay | 99% |
4-Nitrophenyl α-D-galactopyranoside (PNP-alpha-D-Gal) is an artificial substrate of 4-nitrophenyl (pNP) glycopyranoside for the detection of α-galactosidase activity. The amount of released pNP was significantly increased when 4-Nitrophenyl α-D-galactopyranoside was used as a substrate.
Using4-nitorophenol (pNP) -glycopyranosidesaspseudosubstrates, theamountofliberatedpNPfromthe4-Nitrophenylα-D-galactopyranosideissignificantlyhigherthanthatfromtheotherpNP-glycopyranosidesatpH4.0whereasnoactivitywasdetectedatpH7.Chemicalbook0.Thedigestionassaysusing4-nitrophenyl (pNP) glycopyranosidesasartificialsubstratesshowsthatyieldinliberatedgalactoseresiduesfrom4-Nitrophenylα-D-galactopyranosidemainlyatpH4.0, i.e.thepHlevelwhereyieldthresholdisdecreasedatmost.
Substrate of α-D-galactosidase (α-D-Galactosidase). Binds to the E. coli lactose protein carrier. Medium for α-D-galactose.
A rapid method for assessing the lytic activity of antimicrobial agents against yeast and fungi has been developed. The assay is based on the release of the intracellular enzyme, maltase (alpha-glucosidase). The released maltase activity was measured colorimetrically by the production of p-nitrophenol from p-nitrophenyl-alpha-D-glucopyranoside (PNPG). The lytic activity of different antimicrobial compounds was measured against yeast cells or germinating spores of filamentous fungi. Lytic anti-yeast activity could be detected within 20 min incubation at 30 degrees C against Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Candida albicans, and Cryptococcus neoformans. Lytic anti-fungal activity appeared after 2 h of incubation at 30 degrees C against germinating spores of Aspergillus niger and Botrytis cinerea. Whole cells of either yeast or fungi did not hydrolyze sufficient PNPG within 3 h at 30 degrees C to yield a detectable color change. Lytic activity of enzymes (e.g., Lyticase), antibiotics (e.g., Amphotericin B), and an antibiotic-producing strain of bacteria were detected using the assay. The anti-yeast assay has been adapted to a 96-well microtiter format. Both assays provided a rapid, sensitive, and reproducible detection of lytic anti-yeast and anti-fungal activity.