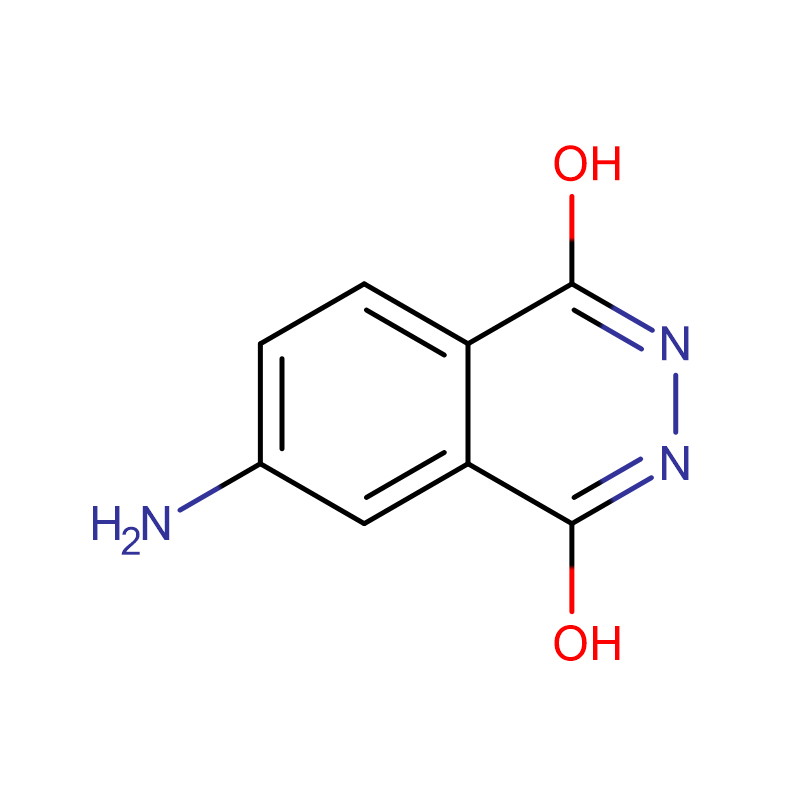
4-Aminophthalhydrazide AMPPD Cas:3682-14-2 Light yellow to amber to dark green powder to lump
| Catalog Number | XD90156 |
| Product Name | 4-Aminophthalhydrazide |
| CAS | 3682-14-2 |
| Molecular Formula | C8H7N3O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 177.16 |
| Storage Details | Store at RT |
Product Specification
| Appearance | Light yellow to amber to dark green powder to lump |
| Assay | ≥98.0% |
| Density | 1.433 |
| Melting point | 300 ºC |
| Boiling point | 633°C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash point | 336.7°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in ammonium hydroxide, sodium carbonate or other base. |
1.We analysed and compared the effect of five H1-antihistamines on stimulated oxidative burst at extra- and intracellular level of isolated and stimulated human polymorphonuclear leukocytes.Oxidative burst of isolated human neutrophils was studied by means of luminol and isoluminol enhanced chemiluminescence.The following rank order of potency for H1-antihistamines to decrease chemiluminescence was evaluated extracellularly: dithiaden> loratadine> chlorpheniramine> brompheniramine> pheniramine and at intracellular site: loratadine> dithiaden.H1-antihistamines differ substantially according to their chemical structure in suppressing oxidative burst both at extra- and intracellular site of isolated stimulated human neutrophils.
2.Chemiluminescence systems enhanced by either isoluminol or luminol in combination with a peroxidase are sensitive methods for the detection of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated by phagocyte NADPH oxidase. The two amplifying substrates are structurally very similar, differing only in the position of the amino group in the aromatic ring of the molecules. This difference renders isoluminol a less lipophilic molecule that is less permeable to biological membranes. The use of isoluminol is consequently restricted to studies dealing with the secretion of oxygen metabolites. In this study we show that synthetic peptides derived from the N-terminal domain of the calcium-regulated protein annexin AI interfere with the detection of radicals in an isoluminol-amplified, but not in a luminol-amplified, system. The annexin AI-derived peptides reduce the light output with isoluminol excited by superoxide and horseradish peroxidase (HRP) in formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine- and phorbol my ristate acetate-stimulated cells, as well as by hydrogen peroxide and HRP. The precise mechanism for the inhibition is not known. The results presented strongly suggest that a reduced cellular response detected with isoluminol-amplified chemiluminescence should be confirmed with an alternative technique to determine release of superoxide anions and hydrogen peroxide.