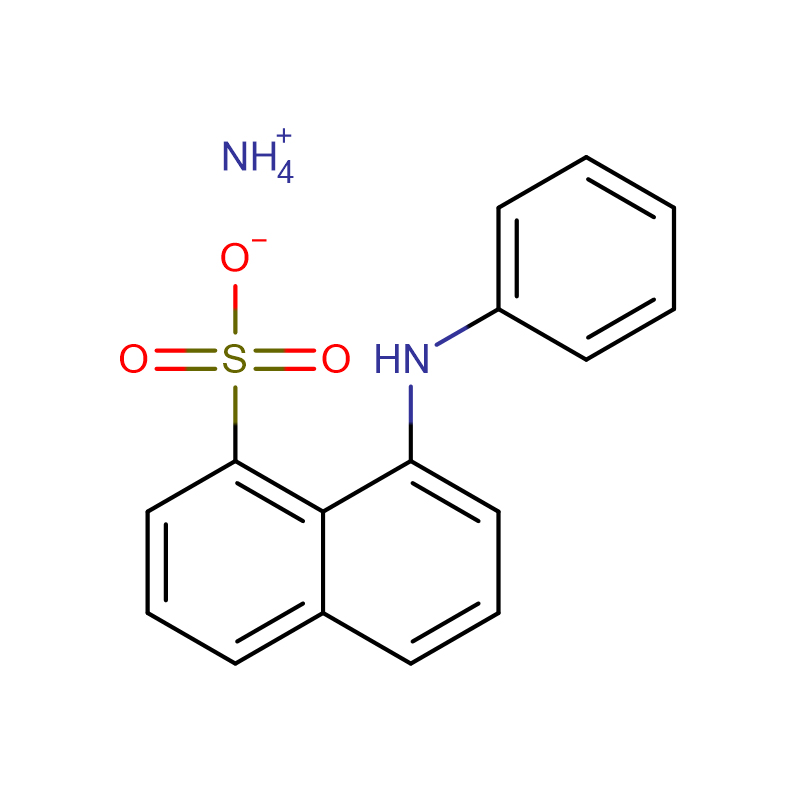
4-Amino-3-hydrazino-1,2,4-triazol-5-thiol Cas:28836-03-5 99% Yellow to green solid
| Catalog Number | XD90146 |
| Product Name | 4-Amino-3-hydrazino-1,2,4-triazol-5-thiol |
| CAS | 28836-03-5 |
| Molecular Formula | C16H13NO3S·NH3 |
| Molecular Weight | 316.37 |
| Storage Details | Ambient |
| Harmonized Tariff Code | 2923900090 |
Product Specification
| Appearance | Yellow to green solid |
| Assay | ≥ 99% |
| Melting point | 237°C(dec.)(lit.) |
| Solubility | NaOH: soluble1 N |
| Water soluble | Soluble in water, 1N NaOH, and methanol. |
1.We studied the inhibitory effects of isorhamnetin on mushroom tyrosinase by inhibition kinetics and computational simulation. Isorhamnetin reversibly inhibited tyrosinase in a mixed-type manner at Ki=0.235±0.013 mM. Measurements of intrinsic and 1-anilinonaphthalene-8-sulfonate(ANS)-binding fluorescence showed that isorhamnetin did not induce significant changes in the tertiary structure of tyrosinase. To gain insight into the inactivation process, the kinetics were computed via time-interval measurements and continuous substrate reactions. The results indicated that inactivation induced by isorhamnetin was a first-order reaction with biphasic processes. To gain further insight, we simulated docking between tyrosinase and isorhamnetin. Simulation was successful (binding energies for Dock6.3: -32.58 kcal/mol, for AutoDock4.2: -5.66 kcal/mol, and for Fred2.2: -48.86 kcal/mol), suggesting that isorhamnetin interacts with several residues, such as HIS244 and MET280. This strategy of predic ting tyrosinase interaction in combination with kinetics based on a flavanone compound might prove useful in screening for potential natural tyrosinase inhibitors.
2.Acid unfolding pathway of conalbumin (CA), a monomeric glycoprotein from hen egg white, has been investigated using far- and near-UV CD spectroscopy, intrinsic fluorescence emission, extrinsic fluorescence probe 1-anilino-8-napthalene sulfonate (ANS) and dynamic light scattering (DLS). We observe pH-dependent changes in secondary and tertiary structure of CA. It has native-like α-helical secondary structure at pH 4.0 but loss structure at pH 3.0. The CA existed exclusively as a pre-molten globule state and molten globule state in solution at pH 4.0 and pH 3.0, respectively. The effect of pH on the conformation and thermostability of CA points toward its heat resistance at neutral pH. DLS results show that MG state existed as compact form in aqueous solutions with hydrodynamic radii of 4.7 nm. Quenching of tryptophan fluorescence by acrylamide further confirmed the accumulation of an intermediate state, partly unfolded, in-between native and unfolded states.