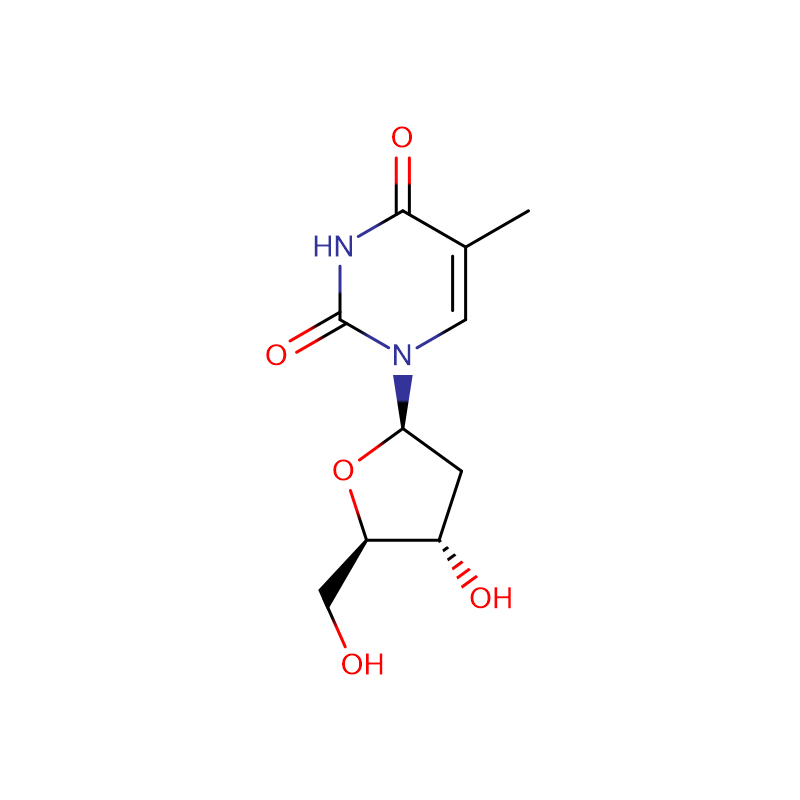
2′-Deoxythymidine Cas:50-89-5
| Catalog Number | XD90582 |
| Product Name | 2'-Deoxythymidine |
|
CAS |
50-89-5 |
|
Molecular Formula |
C10H14N2O5 |
|
Molecular Weight |
242.23 |
| Storage Details | Ambient |
| Harmonized Tariff Code | 29349990 |
Product Specification
| Appearance | White to off-white powder |
| Assay | 99% |
| Loss on Drying | <0.5% |
| Residue on Ignition | <0.3% |
| Specific optical rotation | +17.5 - +19.5 |
We previously encountered regulatory processes wherein dihydrotestosterone (DHT) exerted its inhibitory effect on parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) gene repression through the estrogen receptor (ER)α, but not the androgen receptor (AR), in breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Here, we investigated whether such aberrant ligand-nuclear receptor (NR) interaction is present in prostate cancer LNCaP cells. First, we confirmed that LNCaP cells expressed large amounts of AR at negligible levels of ERα/β or progesterone receptor. Both suppression of PTHrP and activation of prostate-specific antigen genes were observed after independent administration of 17β-estradiol (E2), DHT, or R5020. Consistent with the notion that the LNCaP AR lost its ligand specificity due to a mutation (Thr-Ala877), experiments with siRNA targeting the respective NR revealed that the AR monopolized the role of the mediator of shared hormone-dependent regulation, which was invariably associated with nuclear translocatio n of this mutant AR. Microarray analysis of gene regulation by DHT, E2, or R5020 disclosed that more than half of the genes downstream of the AR (Thr-Ala877) overlapped in the LNCaP cells. Of particular interest, we realized that the AR (wild-type [wt]) and AR (Thr-Ala877) were equally responsible for the E2-AR interactions. Fluorescence microscopy experiments demonstrated that both EGFP-AR (wt) and EGFP-AR (Thr-Ala877) were exclusively localized within the nucleus after E2 or DHT treatment. Furthermore, reporter assays revealed that some other cancer cells exhibited aberrant E2-AR (wt) signaling similar to that in the LNCaP cells. We herein postulate the presence of entangled interactions between wt AR and E2 in certain hormone-sensitive cancer cells.